Introduction
Handling cytotoxic materials presents a critical concern in healthcare, given the significant risks posed to both staff and patients. Implementing best practices for safe management not only protects health but also ensures compliance with evolving regulations. However, the complexities involved in establishing effective protocols raise an important question: how can healthcare facilities navigate the challenges of safe handling, personal protective equipment, and waste management? This article explores essential strategies for creating a comprehensive framework that enhances safety and efficacy in managing these hazardous substances.
Establish Safe Handling Protocols for Cytotoxic Materials
To establish effective safe handling protocols for cytotoxic materials, healthcare facilities should take the following steps:
-
Develop Written Procedures: It is essential to create detailed written guidelines that outline the steps for managing, storing, and disposing of hazardous substances. These guidelines must include specific instructions for various types of medications that contain cytotoxic material and their associated risks.
-
Designate Responsible Personnel: Assigning trained staff to oversee the management of hazardous substances is crucial. This responsibility includes ensuring that all personnel involved are aware of their roles and the established protocols related to cytotoxic material.
-
Implement Engineering Controls: Utilizing engineering controls, such as biological safety cabinets (BSCs) or closed-system drug transfer devices (CSTDs), is vital to minimize exposure during drug preparation and administration.
-
Regularly Review and Update Protocols: Conducting periodic reviews of the protocols is necessary to incorporate new research findings, regulatory changes, and feedback from staff. This practice ensures ongoing effectiveness and compliance.
Implement Personal Protective Equipment Guidelines
To effectively implement PPE guidelines for handling cytotoxic materials, healthcare facilities should take the following steps:
-
Select Appropriate PPE: It is essential that all personnel handling cytotoxic material wear suitable PPE. This includes:
- Nitrile or latex gloves that comply with ASTM D-6978 standards for chemotherapy handling.
- Disposable gowns made of low-permeability fabric, featuring long sleeves and elastic cuffs to minimize exposure.
- Eye protection, such as goggles or face shields, to guard against splashes.
- Respiratory protection when there is a risk of aerosolization.
- Surgical masks when handling medications in a biological safety cabinet to prevent contamination.
-
Educate Staff on Proper Use: Comprehensive training sessions on the correct donning and doffing of PPE are crucial to prevent contamination. This training should be integrated into the initial onboarding process and reinforced through ongoing education. Studies indicate that workplaces with strict PPE enforcement achieve compliance rates as high as 90%. Additionally, addressing discomfort-often the leading reason workers avoid using PPE-is vital to fostering a culture of safety.
-
Regularly Inspect and Replace PPE: Establishing a routine for inspecting PPE for signs of wear and tear is necessary. Damaged items should be replaced immediately. Proper use of PPE can reduce workplace injuries by up to 60%, significantly decreasing incidents of eye injuries, respiratory conditions, and hand injuries. Regular inspections help maintain safety standards and ensure that all protective equipment is functioning effectively. Furthermore, a spill management kit for cytotoxic material should be readily available in all areas where hazardous drugs are handled to address any accidental spills promptly.
Adopt Effective Waste Management Practices for Cytotoxic Materials
To implement effective waste management practices for cytotoxic materials, healthcare facilities must prioritize the following key strategies:
-
Segregate Waste: It is essential to clearly separate hazardous waste from other medical waste streams. This can be achieved by utilizing designated containers with purple lids or bags, which should be clearly labeled to prevent cross-contamination and ensure easy identification.
-
Use Appropriate Disposal Methods: Toxic waste must be disposed of in accordance with local regulations, typically through high-temperature incineration or specialized hazardous waste disposal services. This approach significantly reduces the volume of waste, including cytotoxic material, and minimizes environmental impact.
-
Train Staff on Waste Management: Comprehensive training for personnel on the proper procedures for managing and disposing of hazardous waste is crucial. This training should include protocols for managing spills and leaks, ensuring that all personnel are equipped to respond effectively to potential exposure incidents.
-
Maintain Documentation: Keeping meticulous records of waste disposal activities, including the types and quantities of hazardous waste generated, is vital. Accurate documentation is essential for compliance with regulatory requirements and facilitates traceability in waste management processes.
By adhering to these best practices, healthcare facilities can enhance safety in medical waste disposal and mitigate the risks associated with improper management of hazardous substances.

Provide Comprehensive Training on Cytotoxic Material Handling
To ensure the safe handling of cytotoxic materials, healthcare facilities must adopt a comprehensive training approach that includes several key elements:
-
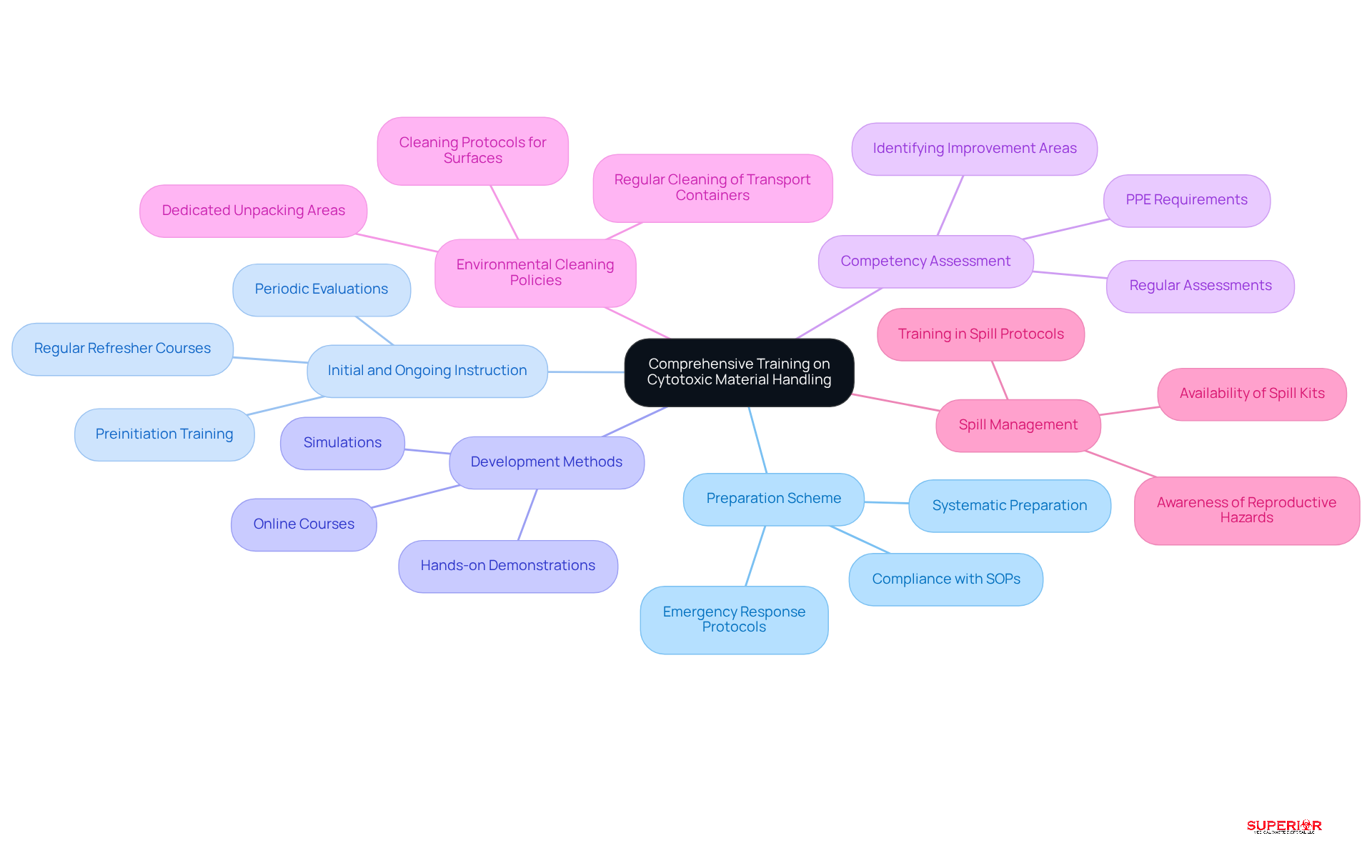
Create a Preparation Scheme: Establish a systematic preparation scheme that addresses all aspects of hazardous substance management, including associated risks, safe methods, and emergency response protocols. Compliance with established standard operating procedures, along with adequate initial and ongoing education in the safe management and administration of cytotoxic material, is essential for minimizing exposure and risk, as emphasized by the Cytotoxic Management Expert Panel.
-
Conduct Initial and Ongoing Instruction: Personnel involved in managing hazardous substances should receive initial instruction before starting their duties, followed by regular refresher courses to stay updated on best practices and regulatory changes. Fernando Moreira, PhD, notes that education in cytotoxic drug handling typically involves preinitiation training and periodic evaluations.
-
Utilize Various Development Methods: Employ a diverse range of techniques, including hands-on demonstrations, online courses, and simulations, to cater to different learning preferences and enhance knowledge retention. The integration of theoretical and practical learning is crucial for effective education.
-
Assess Competency: Conduct regular competency assessments to evaluate staff understanding and their ability to implement safe handling practices effectively. These assessments are vital for identifying areas needing improvement and ensuring compliance with safety standards. Additionally, specific personal protective equipment (PPE) is required for various steps in the medication circuit, highlighting the necessity for thorough training.
-
Implement Environmental Cleaning Policies: Establish cleaning policies for all surfaces that may come into contact with hazardous drugs, including areas designated for unpacking, storage, preparation, and disposal. This is critical for maintaining a safe environment and minimizing contamination risks.
-
Prepare for Spill Management: Ensure that a spill management kit is readily available in all areas where hazardous drugs are stored, handled, or administered. Staff must be informed about the potential reproductive hazards of these drugs and trained in spill management protocols.
By prioritizing these training components, healthcare facilities can significantly mitigate the risks associated with cytotoxic material, thereby protecting both staff and patients.
Conclusion
Establishing safe handling practices for cytotoxic materials is crucial for the protection of healthcare workers and patients. By implementing comprehensive protocols, healthcare facilities can significantly mitigate the risks associated with these hazardous substances. A robust safety framework is built on structured procedures, personal protective equipment (PPE), effective waste management, and thorough training.
Key strategies include:
- Developing written procedures to guide the management of cytotoxic materials
- Selecting and properly using appropriate PPE
- Implementing effective waste disposal methods
Training staff on these protocols equips everyone involved with the necessary knowledge and skills to reduce risks. Regular reviews and updates to these practices further enhance safety and ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
Ultimately, the commitment to safe handling practices for cytotoxic materials transcends mere compliance; it fosters a culture of safety within healthcare environments. By prioritizing these best practices, facilities can safeguard their staff and patients from the dangers of cytotoxic exposure. Embracing these guidelines is a critical step toward ensuring a safer healthcare system for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key steps to establish safe handling protocols for cytotoxic materials?
The key steps include developing written procedures, designating responsible personnel, implementing engineering controls, and regularly reviewing and updating protocols.
Why is it important to develop written procedures for handling cytotoxic materials?
Developing written procedures is essential to provide detailed guidelines for managing, storing, and disposing of hazardous substances, ensuring safety and compliance.
Who should be responsible for overseeing the management of hazardous substances?
Trained staff should be designated to oversee the management of hazardous substances, ensuring all personnel are aware of their roles and the established protocols.
What types of engineering controls are recommended for minimizing exposure to cytotoxic materials?
Recommended engineering controls include biological safety cabinets (BSCs) and closed-system drug transfer devices (CSTDs) to minimize exposure during drug preparation and administration.
How often should protocols for handling cytotoxic materials be reviewed and updated?
Protocols should be reviewed and updated regularly to incorporate new research findings, regulatory changes, and feedback from staff to ensure ongoing effectiveness and compliance.
