Introduction
Healthcare facilities encounter a critical challenge in managing a diverse array of biomedical waste, which can pose significant health and environmental risks if not handled appropriately. This article explores four essential disposal methods that not only ensure compliance with stringent regulations but also enhance safety within healthcare settings. As the stakes rise, it is imperative to consider how healthcare facilities can effectively balance regulatory demands with the necessity for sustainable waste management practices.
Identify Types of Biomedical Waste
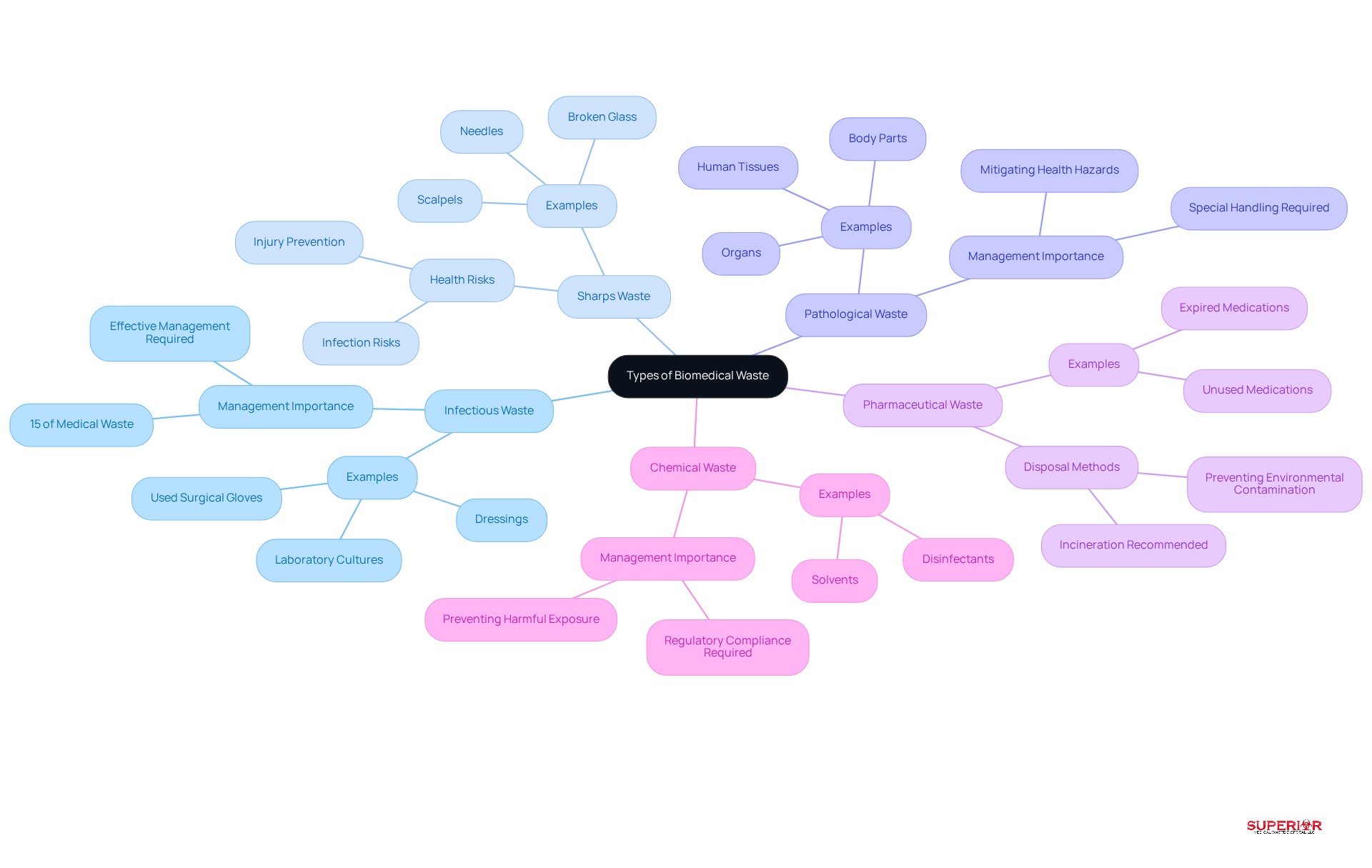
Healthcare facilities generate a diverse array of biomedical waste, which can be categorized into several key groups:
-
Infectious Waste: This category includes materials contaminated with blood, body fluids, or other potentially infectious materials (OPIM). Common examples are used surgical gloves, dressings, and laboratory cultures. Approximately 15% of waste produced by medical activities is classified as hazardous or biohazardous, underscoring the importance of effective management.
-
Sharps Waste: Items that can puncture or cut skin, such as needles, scalpels, and broken glass, fall into this category. Proper elimination is critical to prevent injuries and infections, as mishandling can lead to serious health risks for healthcare workers and patients alike.
-
Pathological Waste: This includes human tissues, organs, and body parts that require special handling and disposal methods. The safe management of pathological waste is essential to mitigate potential health hazards and environmental impacts.
-
Pharmaceutical Waste: Expired or unused medications, including those that are hazardous, must be disposed of according to specific regulations to prevent environmental contamination. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) suggests incineration for pharmaceutical materials to safeguard waterways and the environment.
-
Chemical Waste: This includes hazardous substances utilized in medical environments, such as solvents and disinfectants, which necessitate careful management to prevent harmful exposure. As medical institutions encounter growing regulatory oversight, appropriate classification and elimination of chemical refuse are essential for compliance.
By precisely recognizing these refuse categories, healthcare organizations can adopt customized disposal management strategies that adhere to regulatory standards and safeguard public health. The shift to reusable sharps containers and the implementation of comprehensive pharmaceutical refuse management programs exemplify effective practices that can enhance sustainability and safety in management.
Understand Regulatory Compliance Requirements
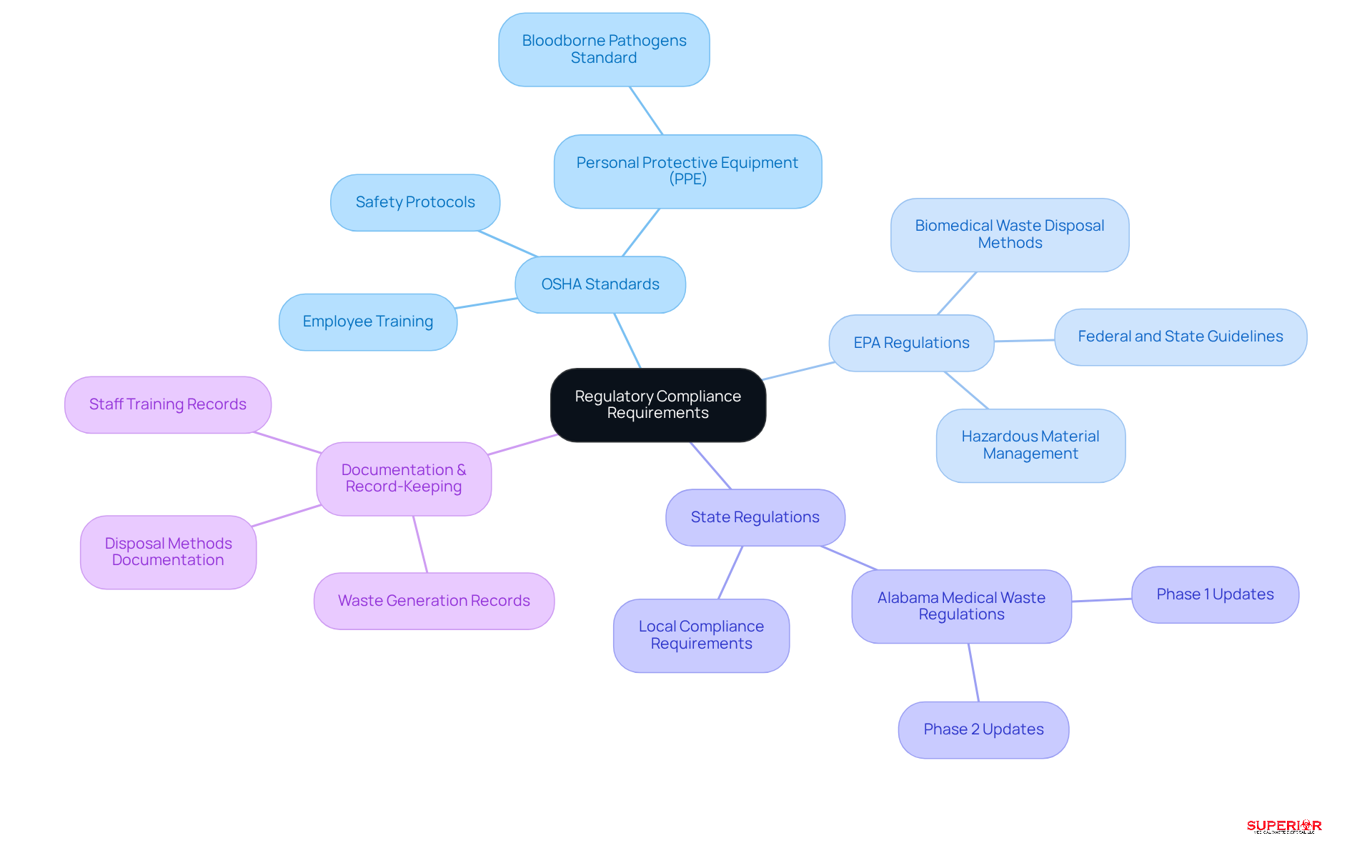
Healthcare institutions must navigate a complex landscape of regulations governing biomedical waste disposal methods. Key compliance requirements include:
-
OSHA Standards: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration mandates that medical facilities implement safety protocols to protect employees from exposure to hazardous materials. This includes proper labeling, thorough training, and the mandatory use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Notably, OSHA’s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard highlights the critical role of PPE in safeguarding healthcare workers from infectious materials, with over 5.5 million workers at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
-
EPA Regulations: The Environmental Protection Agency regulates biomedical waste disposal methods alongside other hazardous materials. Facilities must ensure that waste is treated and disposed of in compliance with federal and state guidelines. Recent updates to EPA regulations aim to streamline hazardous material management processes, thereby enhancing compliance and safety.
-
Each state may impose additional requirements for biomedical waste disposal methods in their regulations. For example, states like Alabama have revised their medical disposal regulations to improve classification and storage practices. Facilities should familiarize themselves with local laws related to biomedical waste disposal methods to ensure comprehensive compliance.
-
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Facilities are required to maintain detailed records of waste generation, disposal methods, and staff training. This documentation is crucial for demonstrating compliance during inspections and mitigating risks associated with improper waste management. Accurate record-keeping not only supports regulatory adherence but also boosts operational efficiency. If you lack a medical or biohazard disposal management plan, we can assist in creating one for you!
By understanding and adhering to these regulatory obligations, medical institutions can effectively mitigate risks associated with improper waste management and enhance their operational efficiency.
Implement Safe and Effective Disposal Methods
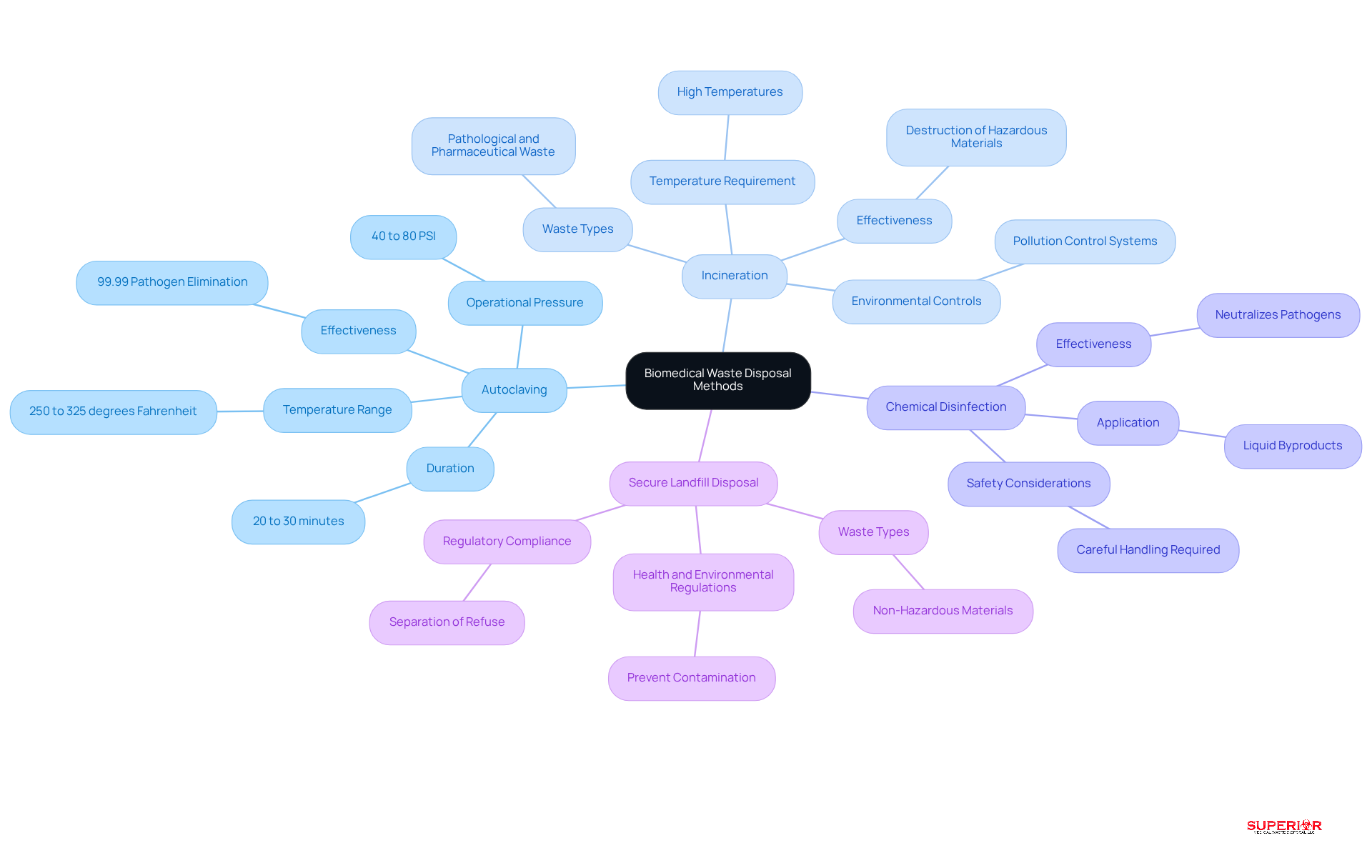
To ensure the safe disposal of biomedical waste, healthcare facilities should consider several effective methods:
-
Autoclaving: This method utilizes high-pressure steam to sterilize infectious materials, rendering them safe for disposal. Operating at temperatures between 250 and 325 degrees Fahrenheit, autoclaving is widely adopted in healthcare settings due to its reliability and efficiency in eliminating pathogens, achieving over 99.99% effectiveness.
-
Incineration: Incineration involves burning refuse at high temperatures, effectively destroying hazardous materials. This method is particularly suitable for pathological and pharmaceutical waste, which accounts for 60-75% of global medical disposal treatment. However, it requires specialized facilities equipped with pollution control systems to minimize environmental impact.
-
Chemical Disinfection: For certain types of waste, chemical disinfection can neutralize pathogens before disposal. This method is commonly applied to liquid byproducts and necessitates careful handling of chemicals to ensure safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
-
Secure Landfill Disposal: Non-hazardous materials can be disposed of in secure landfills that comply with regulatory requirements. It is crucial for establishments to properly separate refuse to prevent contamination and ensure adherence to health and environmental regulations.
By adopting biomedical waste disposal methods, medical institutions can effectively manage biomedical waste, thereby reducing risks to public health and the environment while remaining compliant with evolving regulatory standards.
Provide Staff Training and Education
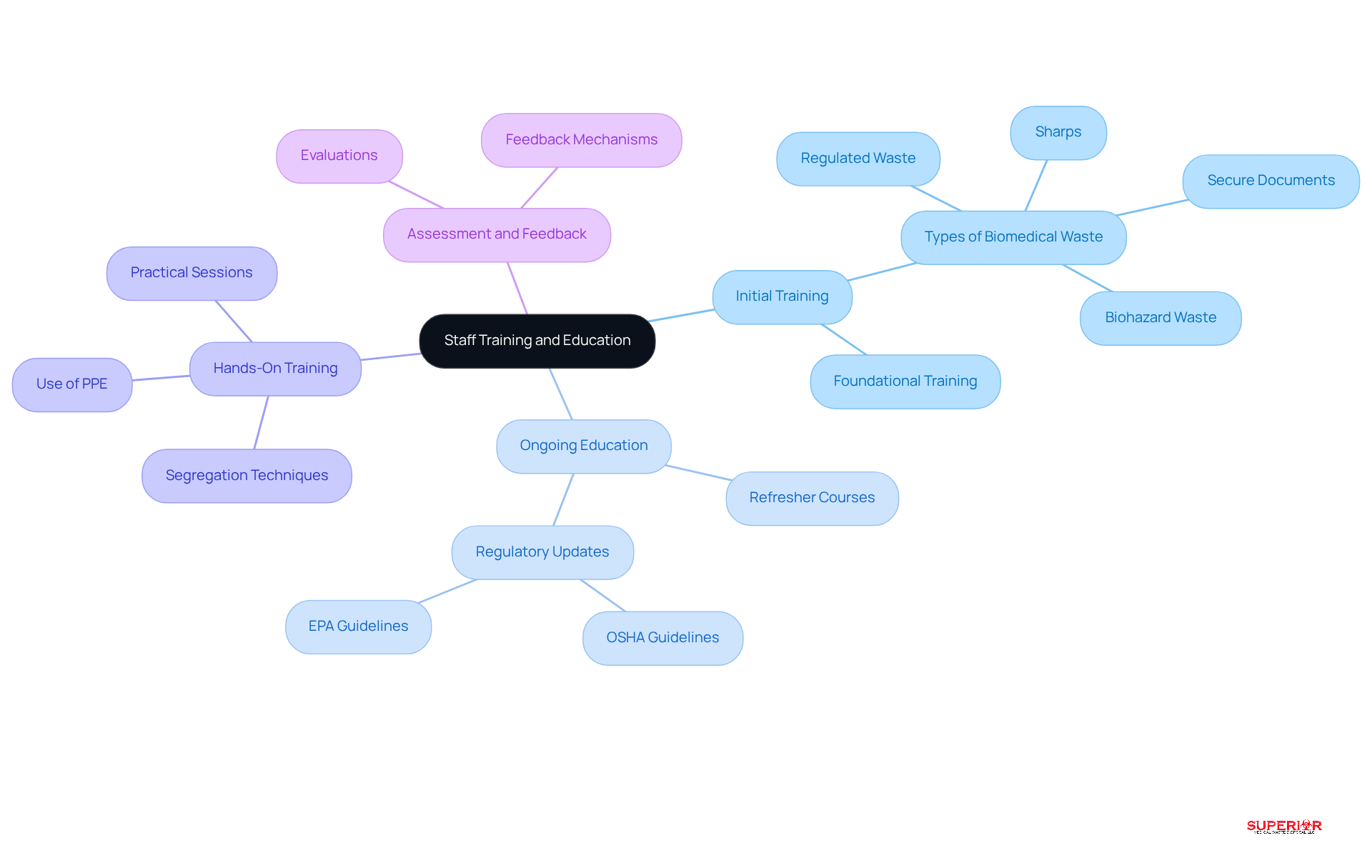
Effective training programs are essential for healthcare personnel involved in biomedical waste disposal methods, particularly in Traverse City, where local healthcare facilities produce significant amounts of medical refuse. A successful training program includes several key components:
-
Initial Training: Comprehensive training must be provided to all new employees, covering the various types of biomedical waste. This includes regulated waste such as medical or pharmaceutical waste, biohazard waste, sharps, and secure documents that require shredding. This foundational training on biomedical waste disposal methods should take place before staff engage in refuse management tasks.
-
Ongoing Education: Regular refresher courses are vital to keep staff informed about evolving regulations and best practices, including the latest OSHA and EPA guidelines. Continuous education fosters a culture of compliance and safety within the organization.
-
Hands-On Training: Practical sessions are crucial for familiarizing staff with the equipment and procedures used in refuse management. Training should emphasize the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and effective segregation techniques to minimize risks, especially concerning regulated materials.
-
Assessment and Feedback: Implementing assessments to evaluate staff understanding and retention of training material is critical. Feedback mechanisms can identify areas for improvement, ensuring that training programs remain effective and relevant.
By prioritizing staff training and education, healthcare facilities can cultivate a culture of safety and compliance, significantly enhancing their practices with biomedical waste disposal methods.
Conclusion
Effective biomedical waste disposal is essential for healthcare facilities, ensuring public safety and environmental protection. By understanding the various types of biomedical waste and implementing appropriate disposal methods, healthcare organizations can significantly mitigate the risks associated with improper waste management. This article underscores the importance of:
- Accurately categorizing waste
- Adhering to regulatory compliance
- Employing safe disposal methods
- Prioritizing staff training
The key arguments presented highlight the necessity for healthcare facilities to:
- Categorize their biomedical waste accurately
- Comply with OSHA and EPA regulations
- Utilize effective disposal techniques such as autoclaving, incineration, and secure landfill disposal
Furthermore, ongoing education and hands-on training for staff are crucial in fostering a culture of safety and compliance, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing health hazards.
In conclusion, as healthcare facilities navigate the complexities of biomedical waste management, it is imperative to adopt best practices that not only meet regulatory standards but also promote sustainability and safety. By prioritizing effective waste management strategies and investing in staff education, healthcare organizations can contribute to a healthier environment and safeguard public health for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of biomedical waste generated by healthcare facilities?
The main types of biomedical waste include Infectious Waste, Sharps Waste, Pathological Waste, Pharmaceutical Waste, and Chemical Waste.
What is Infectious Waste and why is it important to manage it effectively?
Infectious Waste includes materials contaminated with blood, body fluids, or other potentially infectious materials. It is important to manage it effectively because approximately 15% of waste produced by medical activities is classified as hazardous or biohazardous, posing health risks.
What items are classified as Sharps Waste?
Sharps Waste includes items that can puncture or cut skin, such as needles, scalpels, and broken glass. Proper disposal is critical to prevent injuries and infections.
What does Pathological Waste consist of?
Pathological Waste consists of human tissues, organs, and body parts that require special handling and disposal methods to mitigate health hazards and environmental impacts.
How should Pharmaceutical Waste be disposed of?
Pharmaceutical Waste, including expired or unused medications, must be disposed of according to specific regulations, often through incineration, to prevent environmental contamination.
What is Chemical Waste in a healthcare context?
Chemical Waste includes hazardous substances used in medical environments, such as solvents and disinfectants. Careful management is necessary to prevent harmful exposure and ensure regulatory compliance.
Why is it important for healthcare organizations to recognize these waste categories?
Recognizing these waste categories allows healthcare organizations to adopt customized disposal management strategies that adhere to regulatory standards and safeguard public health.
What practices can enhance sustainability and safety in biomedical waste management?
Effective practices include the shift to reusable sharps containers and the implementation of comprehensive pharmaceutical waste management programs.
