Introduction
Understanding the complexities of medical waste management is essential for healthcare facilities that seek to safeguard public health and the environment. The Medical Waste Management Act establishes critical regulations governing the handling, storage, and disposal of medical waste. This presents a significant opportunity for organizations to elevate their operational standards. However, a pressing challenge persists: how can facilities effectively navigate compliance while mitigating the risks associated with improper waste disposal? This article serves as a comprehensive guide, outlining five essential steps to ensure adherence to the Medical Waste Management Act and promote best practices in waste management.
Understand the Medical Waste Management Act
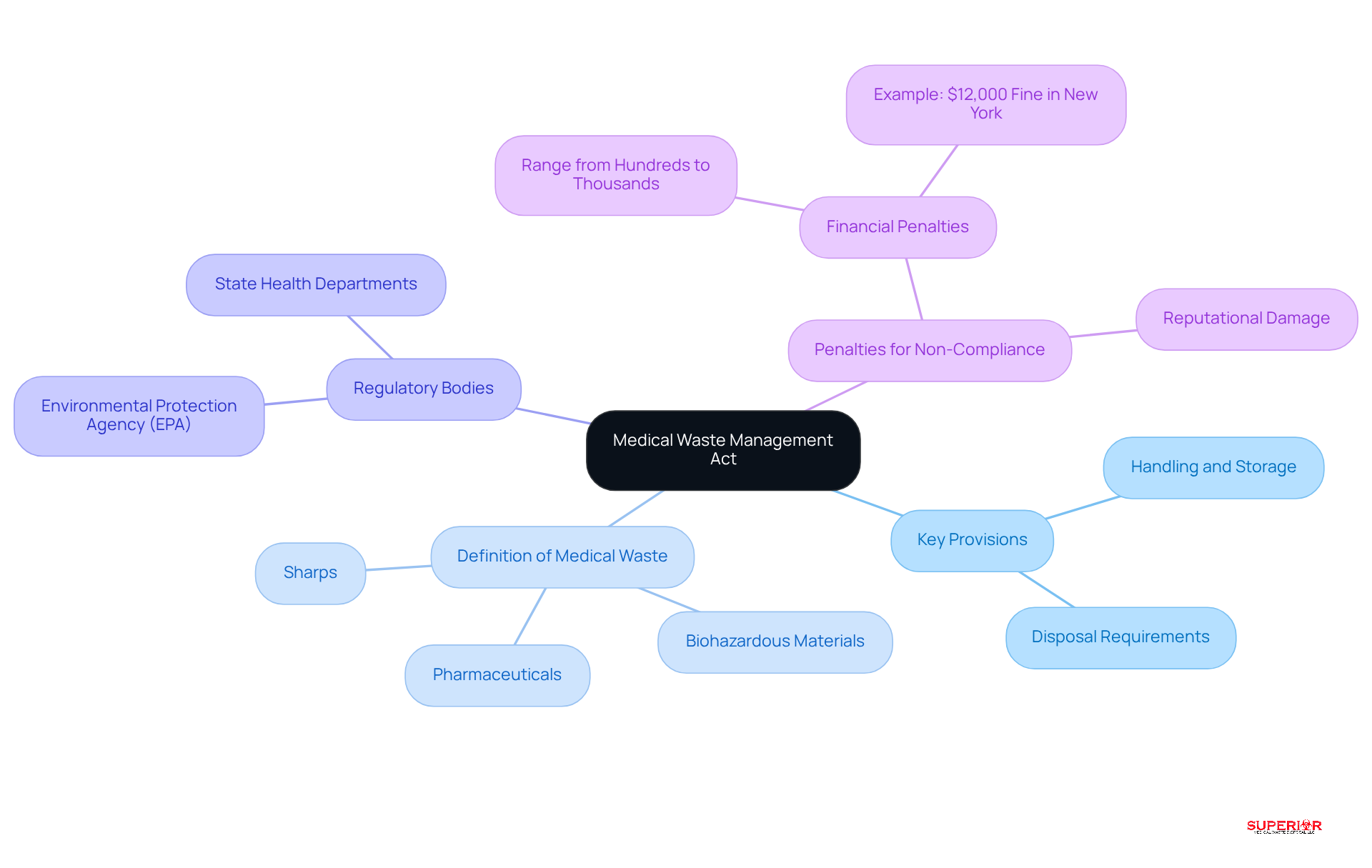
Understanding the key provisions that regulate the handling, storage, and disposal of medical waste is essential to comply with the Medical Waste Management Act. This is crucial for safeguarding public health and the environment.
Definition of Medical Waste: The Act defines medical waste to include sharps, biohazardous materials, and pharmaceuticals. These materials require careful management to prevent harm.
Regulatory Bodies: The enforcement of the Act is under the jurisdiction of agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and state health departments. These bodies supervise adherence to the Act and ensure that facilities follow established standards.
Penalties for Non-Compliance: It is crucial to understand the potential fines and legal repercussions for failing to comply with the Act. Non-compliance can lead to significant financial penalties, which vary based on the severity of the violation, and can also damage an entity’s reputation. Penalties can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars, underscoring the importance of strict adherence to regulations.
By grasping these elements, healthcare facilities can navigate the complexities of medical waste management more effectively and ensure compliance with the medical waste management act.
Identify Types of Medical Waste
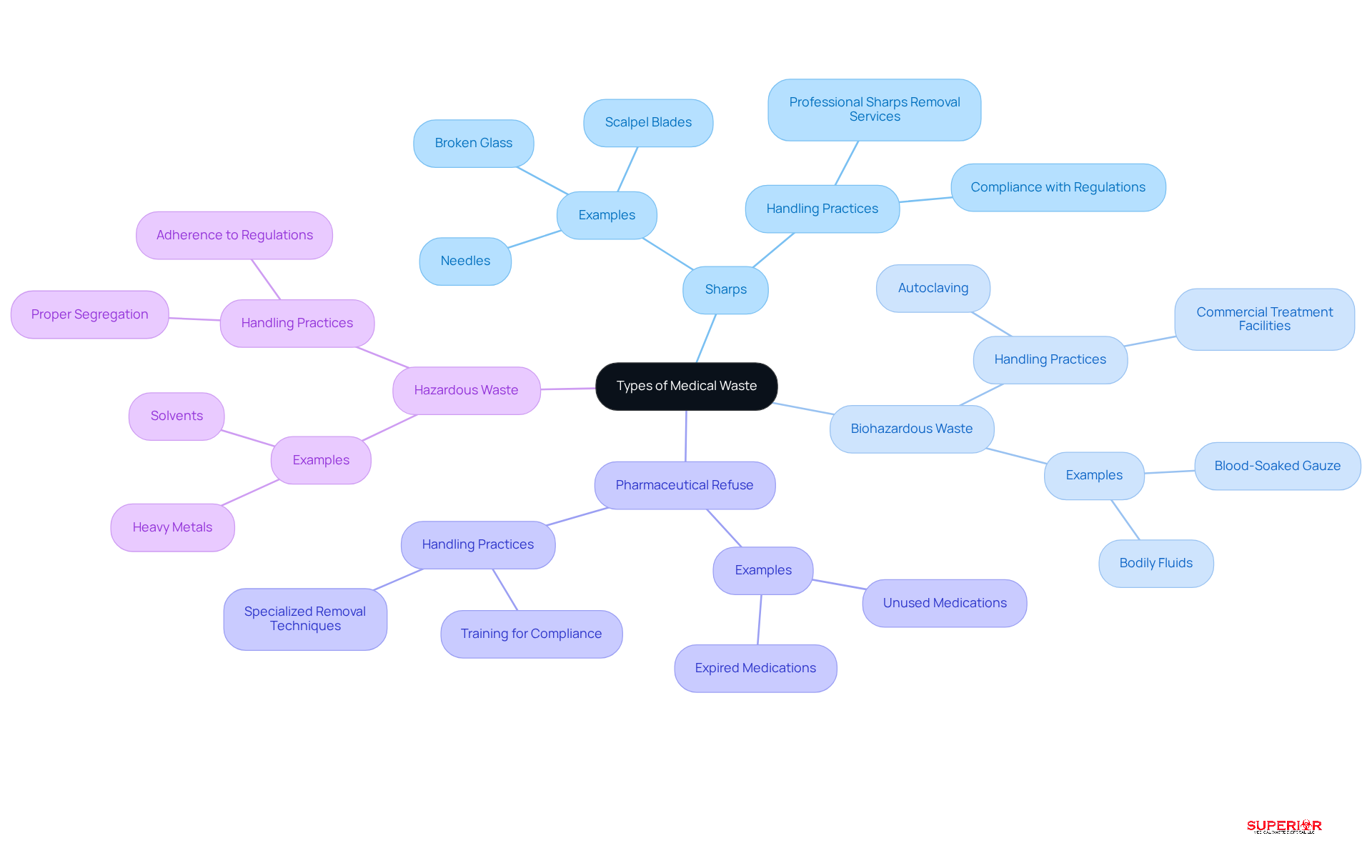
Effective medical waste management act starts with accurately identifying various waste types. The primary categories include:
-
Sharps: This category includes items such as needles, scalpel blades, and broken glass, which pose significant injury risks. In healthcare environments, sharps injuries remain a critical issue, with approximately 16 billion injections administered worldwide each year. This statistic underscores the necessity for appropriate waste management practices. Superior Medical Refuse Management offers professional sharps removal services to ensure safe handling and compliance with regulations.
-
Biohazardous Waste: This encompasses materials contaminated with infectious agents, including blood-soaked gauze and other bodily fluids. Proper handling and disposal are essential to prevent exposure to pathogens. According to Ohio EPA regulations, all infectious wastes should be sent to a commercial treatment facility. At Superior, we utilize autoclaving to effectively treat biohazard waste, ensuring it is disinfected before disposal.
-
Pharmaceutical Refuse: This category includes expired or unused medications, which require specialized removal techniques to minimize environmental impact and prevent misuse. Our pharmaceutical disposal services provide training to ensure that healthcare facilities comply with regulatory standards.
-
Hazardous Waste: This includes chemicals or materials that pose risks to health or the environment, such as solvents and heavy metals from medical devices.
By accurately classifying medical refuse, healthcare facilities can ensure compliance with the medical waste management act and significantly reduce the risks associated with improper disposal management. Best practices involve using designated containers, implementing proper labeling, and following established disposal protocols. As emphasized by the World Health Organization, promoting practices that minimize refuse volume and ensure proper segregation is vital for effective management. Furthermore, with home healthcare projected to reach $176 billion by 2032, the challenges in managing medical waste will continue to escalate, necessitating adherence to evolving regulations, including the medical waste management act in Ohio.
Develop a Customized Waste Management Plan
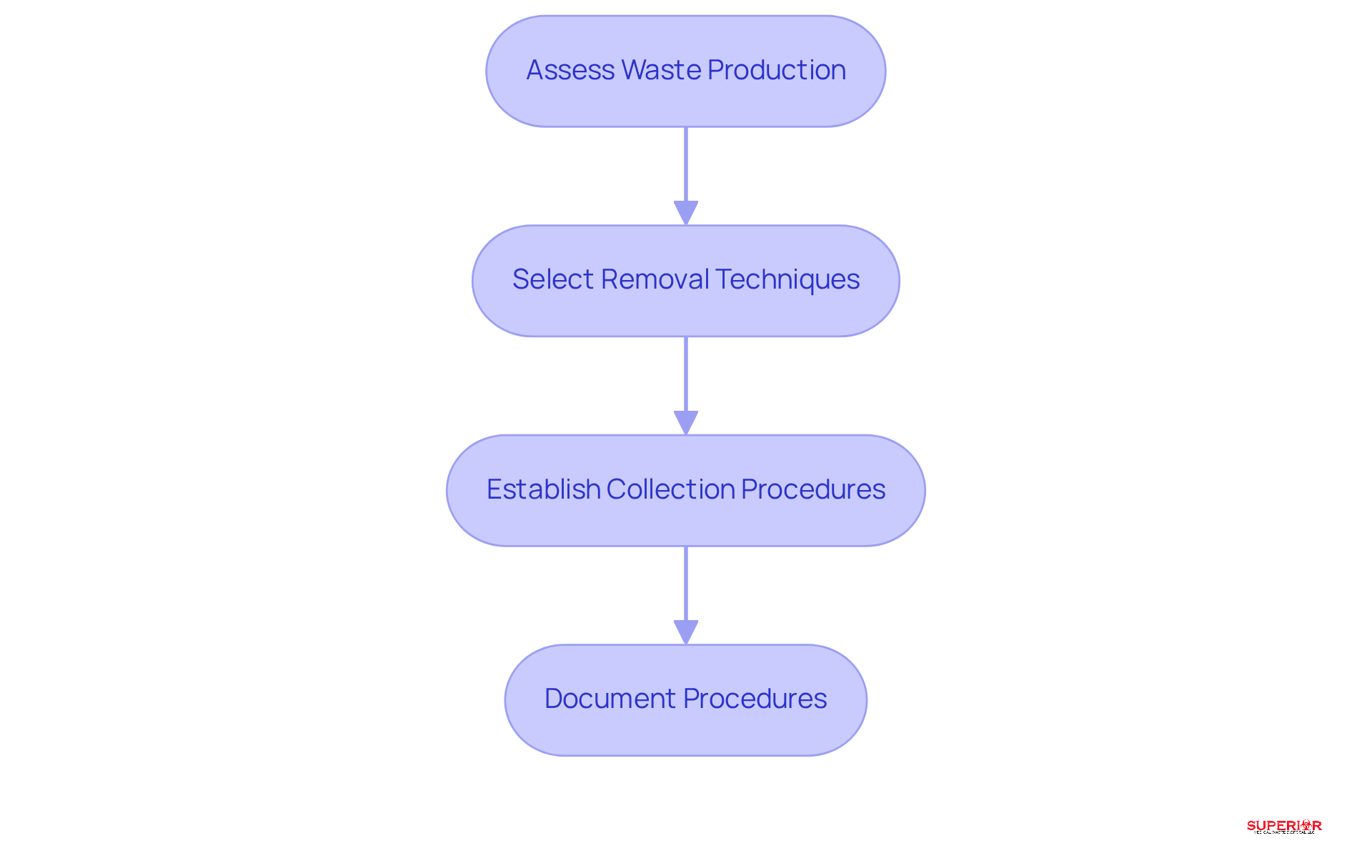
Creating a customized waste management plan in accordance with the medical waste management act involves several essential steps that ensure compliance and enhance operational efficiency.
-
Assess Waste Production: Begin with a thorough evaluation of the types and quantities of medical refuse generated by your facility. This assessment is crucial, as hospitals in the U.S. produce over 14,000 tons of refuse daily, highlighting the need for adherence to the medical waste management act, especially with projections indicating an increase due to expanding healthcare services. Additionally, it is vital to consult your local environmental authority for guidance on the medical waste management act and handling procedures.
-
Select Removal Techniques: Choose appropriate removal methods tailored to each type of refuse. For example, incineration is suitable for biohazardous materials, while sharps must be disposed of in secure, FDA-approved containers. At Superior Medical Disposal, we employ advanced technologies, such as autoclaving and shredding, to treat biohazard materials, effectively reducing their volume by 70% before disposal in a sanitary landfill. This approach aligns with sustainability goals and ensures compliance with local regulations.
-
Establish Collection Procedures: Define clear protocols for how and when refuse will be collected. These protocols should adhere to local regulations, such as the medical waste management act in Michigan, which mandates storing biohazard materials for no more than 90 days prior to proper removal. Consideration of collection frequency is essential to minimize transportation costs and environmental impact.
-
Document Procedures: Maintain comprehensive written records of your refuse management plan, detailing disposal methods and collection schedules. This documentation not only supports compliance but also demonstrates your facility’s commitment to environmental leadership and safety.
By developing a tailored waste management plan in accordance with the medical waste management act, healthcare facilities can effectively manage their waste while ensuring adherence to regulatory standards and promoting sustainability.
Implement Safe Disposal Methods
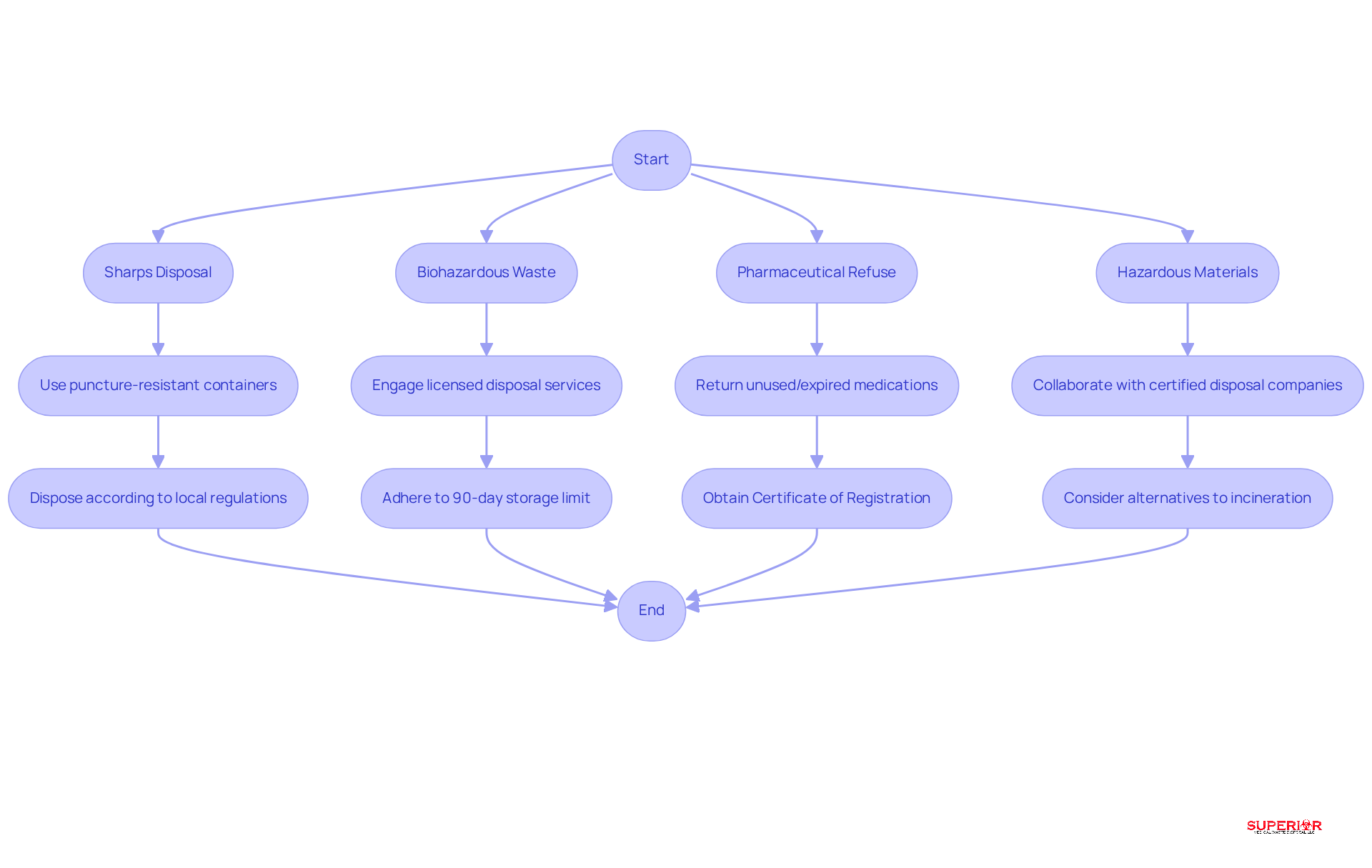
To ensure compliance with the Medical Waste Management Act, healthcare facilities must implement safe disposal methods:
-
Sharps Disposal: Facilities should utilize puncture-resistant containers specifically designed for sharps. It is crucial to dispose of these containers in accordance with local regulations to prevent injuries and infections. Improper handling can lead to sharps-inflicted injuries, which pose significant health risks.
-
Biohazardous Waste: Engage licensed medical waste disposal services, such as those offered by Superior Medical Waste Disposal, for the safe handling of biohazardous materials. These services ensure that waste is treated in compliance with established standards, including autoclaving, which steam heats the waste to eliminate biological threats. Facilities must also adhere to the 90-day storage limit for biohazard materials before proper removal. After treatment, the refuse is classified as ordinary refuse and can be discarded in a sanitary landfill. This process not only mitigates environmental and health risks but also reduces waste volume by up to 70% prior to removal.
-
Pharmaceutical Refuse: Follow specific protocols for pharmaceutical disposal, which involve returning unused or expired medications to sanctioned take-back programs. This practice helps prevent misuse and environmental contamination, addressing the toxic exposure risks associated with improper disposal. Superior Medical Refuse Disposal also provides pharmaceutical disposal handling and removal services, ensuring compliance with OSHA regulations. Additionally, facilities generating medical refuse are required to obtain a Certificate of Registration, which must be renewed every three years.
-
Hazardous Materials: Collaborate with certified hazardous materials disposal companies to manage hazardous substances effectively. These companies are equipped to handle various forms of dangerous materials, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards. Furthermore, consider alternatives to incineration, such as autoclaving and microwaving, to enhance waste management practices.
By following these methods, facilities can significantly reduce risks associated with improper refuse disposal and uphold legal standards, ultimately safeguarding public health and the environment. Additionally, minimizing healthcare waste through green procurement, reusables, and recycling is essential for sustainable waste management.
Train Staff on Compliance and Safety Protocols
Training personnel is crucial for compliance with the Medical Refuse Management Act. To ensure effective training, consider the following steps:
-
Develop tailored training materials that create comprehensive training resources specifically addressing the Medical Waste Management Act. Detail the various types of waste – such as sharps, infectious, chemotherapeutic, and pharmaceutical – and outline their appropriate disposal methods. Regularly update these materials to reflect current regulations and best practices.
-
Conduct Regular Training Sessions: Schedule consistent training sessions for all staff members, emphasizing their specific responsibilities in refuse management. This should include initial training within 30 days of managing refuse, followed by yearly refreshers to reinforce knowledge and adherence.
-
Provide Hands-On Training: Incorporate practical demonstrations that illustrate safe handling and disposal techniques for medical materials. This experiential learning method helps staff understand the importance of proper refuse segregation and the use of color-coded containers, which are essential for compliance with state-specific regulations.
-
Evaluate Understanding: Assess staff knowledge through quizzes or practical evaluations to ensure comprehension of protocols. Tracking performance indicators, such as a decrease in improper waste management incidents, can help evaluate the effectiveness of training programs and identify areas for improvement.
By investing in thorough staff training, healthcare facilities can cultivate a culture of compliance and safety, ultimately reducing risks associated with improper refuse disposal in accordance with the Medical Waste Management Act.
Conduct Regular Audits and Reviews
Healthcare facilities in Traverse City must conduct regular audits and reviews of their waste management practices to ensure compliance with the medical waste management act.
-
Schedule Audits: Establish a consistent audit schedule, ideally quarterly or bi-annually, to evaluate adherence to disposal management protocols. This proactive approach allows facilities, such as Munson and Byers Heather, to identify compliance gaps before they escalate into significant issues. As noted by Medic, “Facilities that start with a medical refuse audit gain a clearer understanding of their position and where minor adjustments can minimize risk.” Superior Medical Disposal specializes in providing tailored solutions for Traverse City healthcare facilities, ensuring they meet local regulations and effectively manage their medical streams.
-
Review Documentation: Thoroughly examine records related to waste disposal, staff training, and waste management plans. Precise and thorough documentation is essential for demonstrating adherence and ensuring that all procedures are followed correctly. Facilities must also ensure that all employees handling bloodborne pathogens have completed the required training as mandated by OSHA, and that this training is documented according to the medical waste management act of the facility.
-
Identify Areas for Improvement: Utilize findings from audits to pinpoint compliance gaps or procedural inefficiencies. Small adjustments, such as refining container strategies or enhancing staff training, can significantly reduce risks associated with improper waste management. Notably, Traverse City healthcare facilities generate thousands of pounds of medical refuse each year, emphasizing the necessity for effective management. Superior Medical Disposal can assist in developing a comprehensive medical management plan tailored to the specific needs of each facility.
-
Implement Changes: Based on audit results, make necessary adjustments to refuse management practices. This may involve updating protocols, enhancing staff training, or improving garbage separation practices to ensure continuous adherence. According to recent statistics, “37% of businesses conduct one or more internal audits per year,” highlighting the significance of regular evaluations.
Regular audits empower facilities to proactively address compliance issues, streamline waste management processes, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Conducting audits in January, for instance, allows facilities to stabilize workflows and evaluate practices without the pressure of peak patient volumes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and complying with the Medical Waste Management Act is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is a vital responsibility that healthcare facilities must adopt to safeguard public health and the environment. By adhering to the prescribed steps, these facilities can effectively manage medical waste, ensuring safe handling, proper disposal, and compliance with legal standards.
This article has highlighted key aspects of compliance, including:
- The necessity of recognizing the various types of medical waste
- Formulating a tailored waste management plan
- Implementing safe disposal methods
- Training staff on compliance protocols
- Conducting regular audits
Each of these steps is crucial for minimizing risks associated with improper waste management and for upholding a facility’s reputation and operational integrity.
Ultimately, prioritizing compliance with the Medical Waste Management Act represents an investment in safety and sustainability. Healthcare facilities are urged to adopt proactive measures in their waste management practices, fostering a culture of compliance through ongoing training and regular evaluations. By doing so, they not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also contribute to a healthier community and a cleaner environment for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Medical Waste Management Act?
The Medical Waste Management Act regulates the handling, storage, and disposal of medical waste to safeguard public health and the environment.
What types of waste are defined as medical waste under the Act?
Medical waste includes sharps, biohazardous materials, and pharmaceuticals, all of which require careful management to prevent harm.
Which agencies are responsible for enforcing the Medical Waste Management Act?
The enforcement of the Act falls under the jurisdiction of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and state health departments.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with the Medical Waste Management Act?
Non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties that vary based on the severity of the violation, ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars, and can also harm an entity’s reputation.
What are the main categories of medical waste that need to be identified?
The main categories of medical waste include sharps, biohazardous waste, pharmaceutical refuse, and hazardous waste.
What items are considered sharps?
Sharps include needles, scalpel blades, and broken glass, which pose significant injury risks in healthcare environments.
What constitutes biohazardous waste?
Biohazardous waste consists of materials contaminated with infectious agents, such as blood-soaked gauze and other bodily fluids.
How should pharmaceutical refuse be managed?
Pharmaceutical refuse, which includes expired or unused medications, requires specialized removal techniques to minimize environmental impact and prevent misuse.
What is considered hazardous waste in a medical context?
Hazardous waste includes chemicals or materials that pose risks to health or the environment, such as solvents and heavy metals from medical devices.
What best practices should healthcare facilities follow for medical waste management?
Best practices include using designated containers, implementing proper labeling, and following established disposal protocols to ensure compliance with the Medical Waste Management Act.
