Introduction
Medical sharps, such as needles and scalpel blades, present significant risks in healthcare settings, often resulting in serious injuries and the potential transmission of bloodborne pathogens. Notably, needlestick incidents account for over 80% of percutaneous exposures among healthcare workers, underscoring the urgent need for effective disposal practices. This article explores best practices for the safe disposal of medical sharps, detailing essential protocols and training strategies that not only safeguard healthcare professionals but also ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
How can healthcare facilities enhance their sharps disposal methods to improve safety and mitigate risks in an evolving regulatory landscape?
Understand Medical Sharps and Their Risks
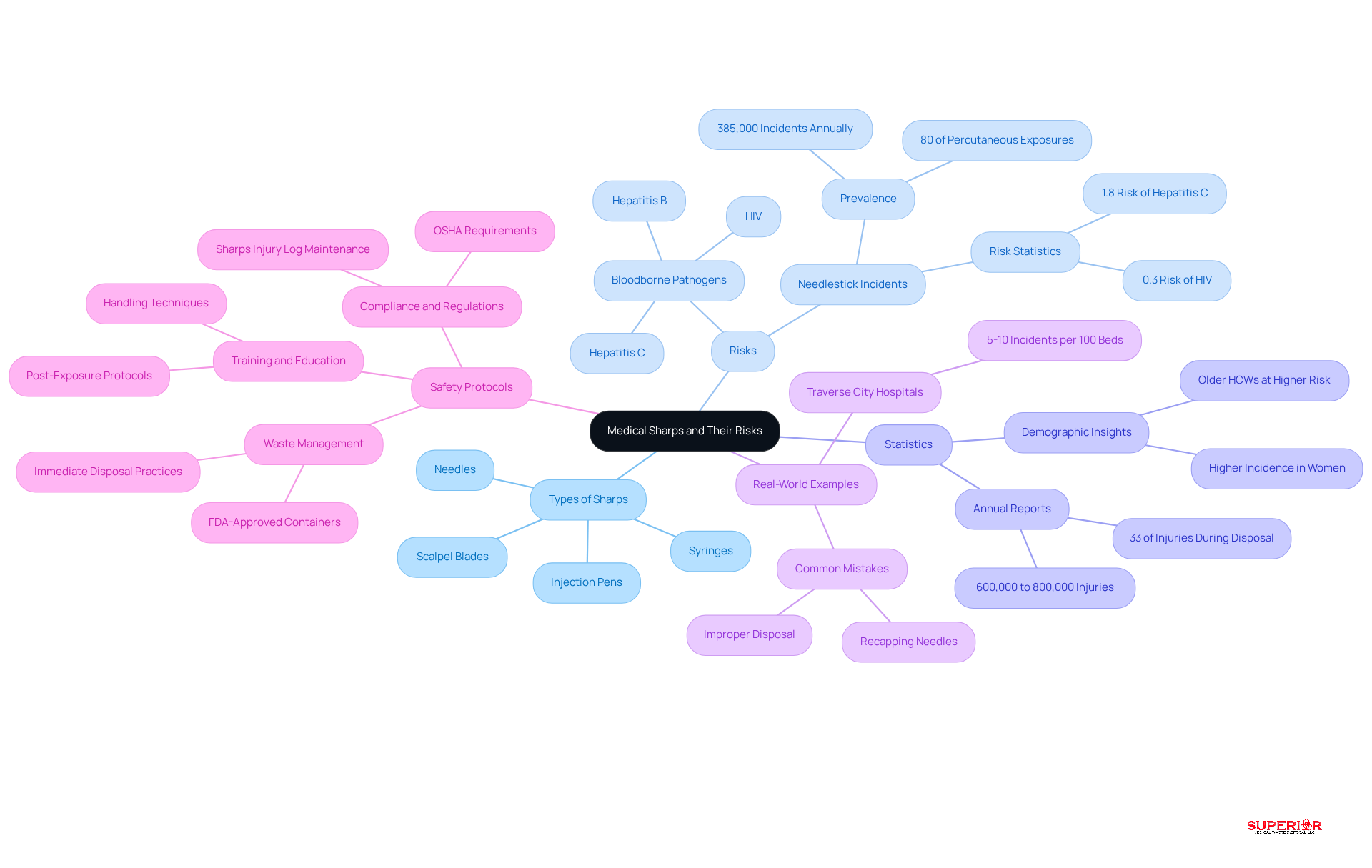
Medical instruments, including medical sharps like needles, syringes, and scalpel blades, present significant risks in medical settings due to their potential to cause needlestick accidents. These injuries are not merely inconveniences; they can lead to the transmission of serious bloodborne pathogens such as HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. According to the CDC, needlestick incidents account for over 80% of all percutaneous exposure occurrences in the United States, underscoring their prevalence as a major occupational hazard for healthcare professionals.
In 2026, the CDC emphasized the importance of understanding the types of needles and their associated hazards to develop effective disposal strategies. For example, approximately 385,000 needlestick incidents and those related to medical sharps are reported annually among healthcare workers, with many cases likely going unreported. The risk of contracting hepatitis C following a sharps incident is about 1.8%, while the risk of HIV transmission is approximately 0.3%. Notably, injection pens are responsible for 39% of needlestick incidents related to subcutaneous injections, highlighting the urgent need for targeted safety measures. These statistics illustrate the critical necessity for comprehensive safety protocols in medical environments.
Real-world examples further illustrate the impact of these injuries. In Traverse City, healthcare facilities, including major hospitals like Munson and Byers Heather, generate substantial amounts of medical waste, including needles. Hospitals report approximately 5-10 needlestick incidents annually per 100 beds, reflecting national trends and the need for local training and awareness. Additionally, research indicates that 33% of all needle-related incidents occur during waste removal, highlighting the vital importance of proper medical sharps handling practices. Hospitals are also mandated to maintain records of needle injuries sustained by workers, which is crucial for compliance and safety.
To mitigate these risks, medical facilities must implement robust waste management protocols for medical sharps, including the use of FDA-approved containers that are closable, puncture-resistant, and leak-proof. Superior Medical Waste Management is dedicated to providing secure and compliant needle removal services tailored to the needs of Traverse City medical facilities. Educating staff on safe handling practices and the importance of prompt disposal after use is essential to protect both healthcare workers and patients from the dangers associated with medical instruments. Furthermore, ongoing training initiatives regarding bloodborne pathogen exposure, as mandated by OSHA, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) as a final safeguard against risks in handling instruments are critical components of a comprehensive safety strategy. Frequent errors in needlestick prevention, such as recapping needles and improper handling, must also be addressed to enhance the safety culture within medical environments.
Implement Safe Disposal Methods for Sharps
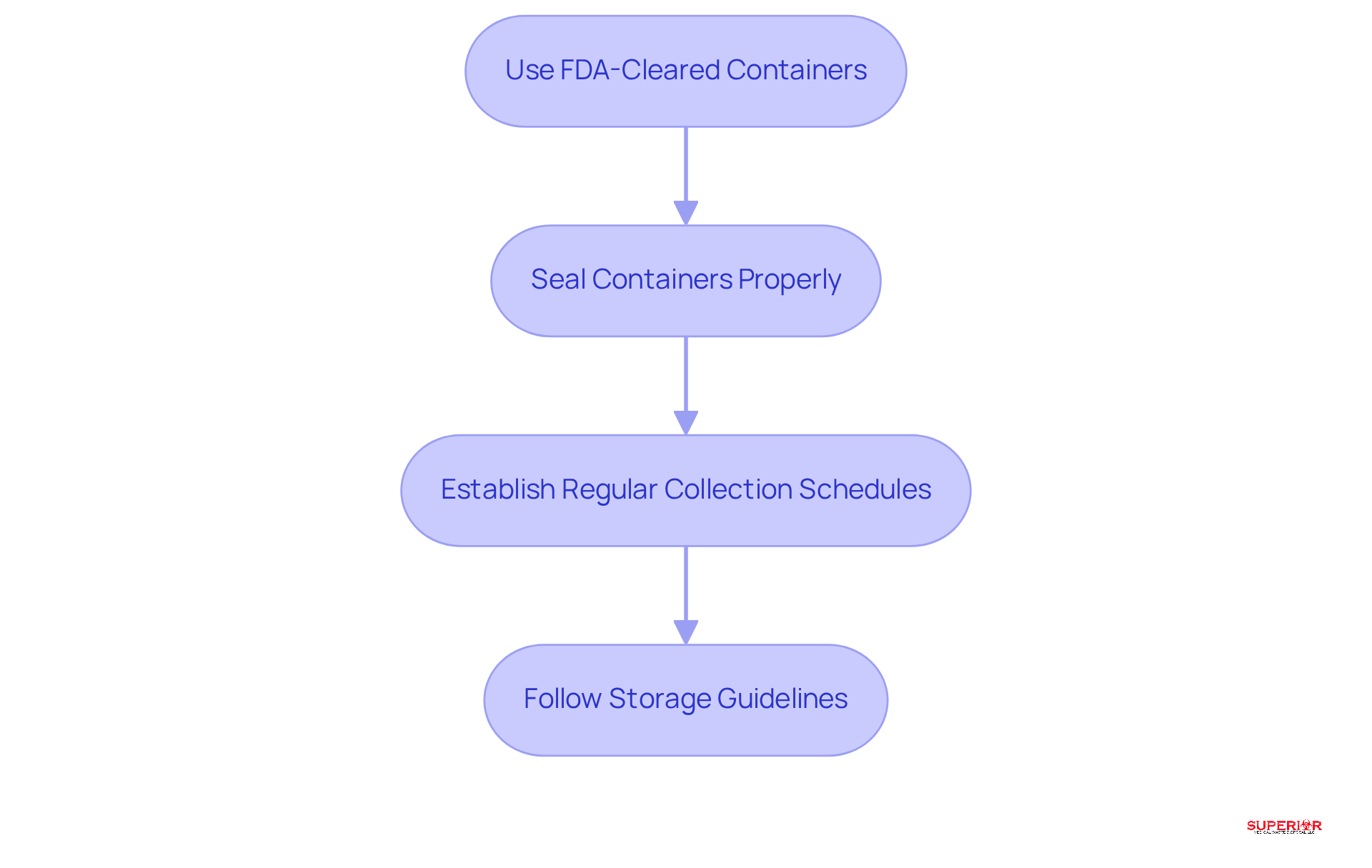
To ensure the safe disposal of sharps, healthcare facilities should adopt the following practices:
-
All medical sharps must be disposed of in FDA-cleared, puncture-resistant, and leak-proof containers. These containers should be positioned close to the point of use to encourage prompt disposal, significantly reducing the risk of needlestick accidents. Research shows that providing easily accessible disposal containers in patient areas and at medication stations can lead to over an 80% reduction in puncture incidents among healthcare personnel.
-
Seal Containers Properly: Once a disposal container reaches its fill line, it must be sealed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This step is essential to prevent spillage during transport of medical sharps and to comply with OSHA regulations, which require containers to be closable and clearly labeled with the biohazard symbol. Containers for medical sharps should be replaced when they are 75% full to prevent needle stick injuries.
-
Establish Regular Collection Schedules: Implement a routine for the collection and removal of full needle containers as part of medical sharps management by a licensed medical waste management service, such as Superior Medical Waste Management, which complies with Ohio EPA regulations. This practice not only prevents overflow but also ensures adherence to local regulations, minimizing the risk of legal liabilities related to improper waste management. Facilities should monitor container fill rates and adjust pickup frequencies based on seasonal needs or surges in waste generation to maintain safety and compliance. Additionally, training on safety equipment handling best practices must be provided to all new employees and existing personnel to emphasize the importance of safety and adherence.
-
Follow Storage Guidelines: It is crucial to maintain the integrity of container systems and ensure they are stored in a manner that prevents them from becoming a food source or breeding area for animals or insects. Containers should be marked with a sign stating “warning: infectious waste” and/or display the international biohazard symbol. Furthermore, infectious waste must remain in a non-putrescent state, utilizing refrigeration or freezing when necessary.
Ensure Compliance with Regulatory Standards
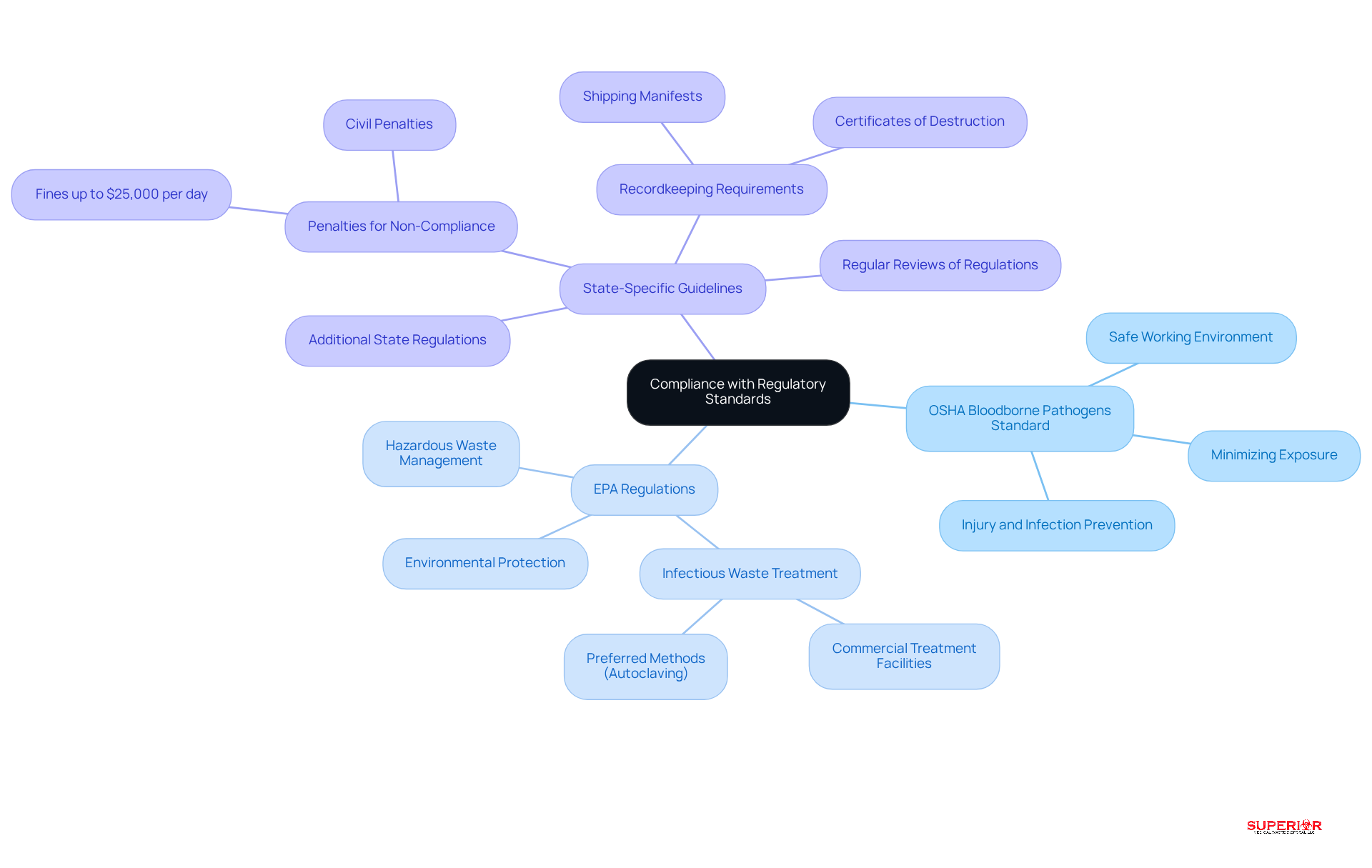
Healthcare facilities must adhere to a complex array of federal and state regulations concerning the management of medical sharps. Key regulations include:
-
OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard: This standard mandates that employers create a safe working environment by implementing measures to minimize exposure to bloodborne pathogens, which encompasses the proper handling of needles. Compliance with this standard is essential for safeguarding healthcare workers from potential injuries and infections.
-
EPA Regulations: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees medical waste management, categorizing medical sharps as hazardous waste under specific circumstances. Facilities must ensure that their waste management practices for medical sharps align with EPA standards to avert environmental contamination and public health risks. For instance, in Ohio, the EPA advises that all infectious waste be directed to a commercial treatment facility, with autoclaving being the preferred method for treating regulated medical waste (RMW). Superior Medical Waste Disposal collaborates with a commercial autoclaving facility to guarantee the safe and compliant treatment of medical waste.
-
State-Specific Guidelines: Various states impose additional regulations that may exceed federal requirements. For example, states like New Hampshire and Pennsylvania have particular mandates regarding the management and disposal of medical sharps, including civil penalties for non-compliance that can reach $25,000 per day. Facilities are also required to maintain shipping manifests and certificates of destruction for a minimum of three to five years to ensure compliance. Some states necessitate weekly pickups of medical waste, which is crucial for operational adherence. Regular reviews of these state regulations are vital for facilities to align their disposal practices with both federal and state laws, thereby reducing risks associated with improper waste management. Furthermore, medical facilities must reassess their pharmaceutical waste protocols in 2026 to stay compliant with evolving regulations.
By remaining informed and compliant with these regulations, healthcare facilities can enhance safety, protect their staff, and contribute to environmental sustainability. Non-compliance can result in substantial penalties and jeopardize the safety of both staff and patients.
Train Staff on Sharps Safety and Disposal Procedures
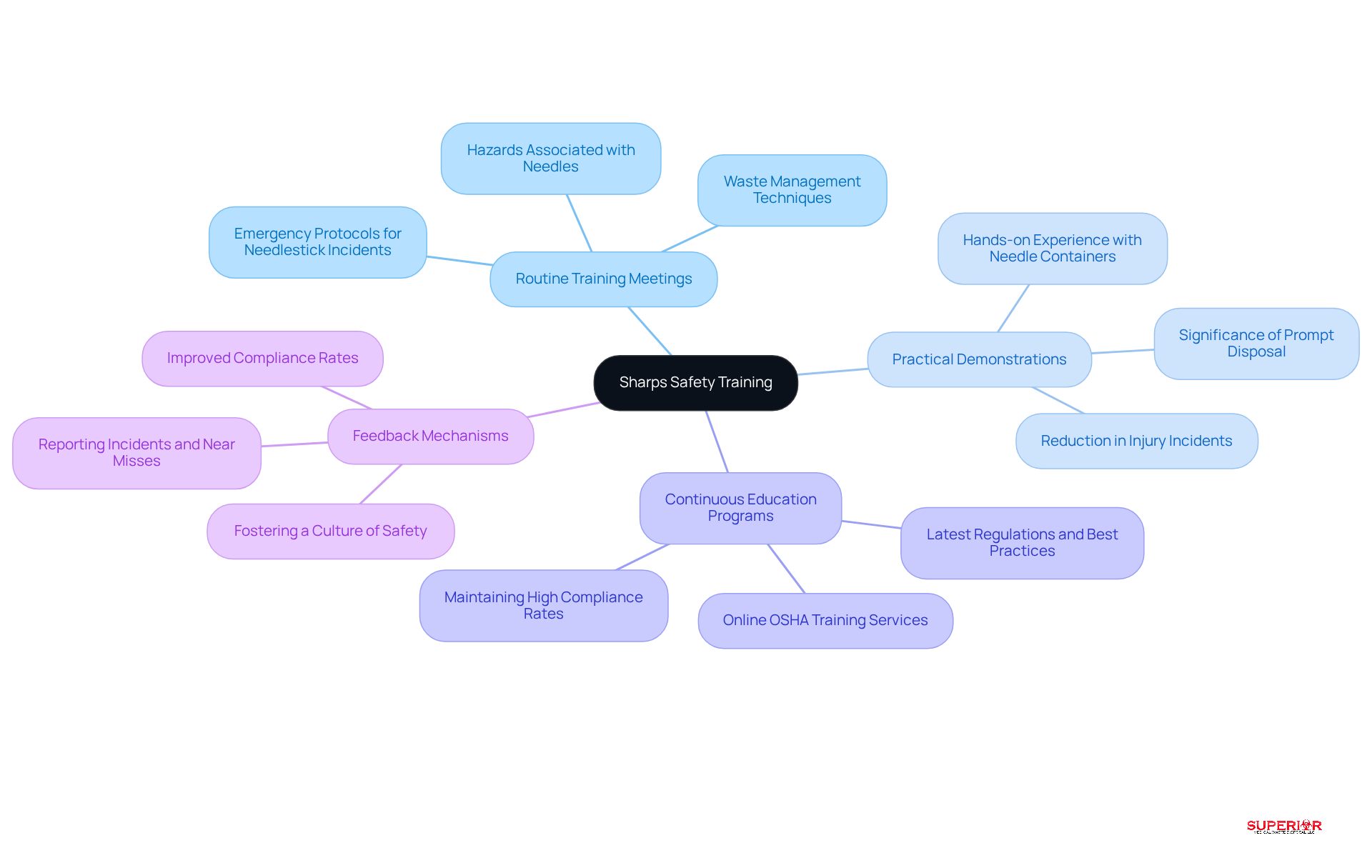
Effective training programs for staff must include several key components to ensure compliance and safety in the disposal of medical sharps.
-
Routine Training Meetings: Training meetings should be organized to address the hazards associated with needles, appropriate waste management techniques, and emergency protocols for needlestick incidents. These sessions are mandatory for all staff, reinforcing the critical importance of safety protocols.
-
Practical Demonstrations: Practical training is essential, allowing staff to effectively practice using needle containers. This hands-on experience is crucial for understanding the significance of prompt disposal, which significantly reduces the risk of injuries. Research shows that nursing technicians experienced a notable decrease in incidents related to inadequate needle management after participating in practical training programs.
Continuous education programs are vital for keeping staff informed about the latest regulations and best practices in medical sharps management. Ongoing learning helps maintain high compliance rates and reinforces the importance of safety measures in the workplace. For instance, Superior Medical Waste Disposal offers an online OSHA training service that covers essential topics such as HIPAA and bloodborne pathogens, ensuring that staff are well-equipped with necessary knowledge.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing a system for staff to provide feedback on disposal practices and report incidents or near misses fosters a culture of safety and continuous improvement. This encourages open communication among team members. Research indicates that organizations with robust feedback systems experience improved compliance rates and a reduction in injuries related to medical sharps.
In 2026, the focus on hands-on training remains crucial, as it directly influences compliance rates and enhances the overall safety culture within healthcare facilities. Experts in the field emphasize that effective training not only protects staff but also ensures adherence to health and safety regulations, ultimately safeguarding patient care.
Conclusion
Implementing safe medical sharps disposal practices is essential for protecting healthcare workers and patients from the significant risks associated with needlestick injuries. By understanding the types of medical sharps and adhering to best practices, healthcare facilities can effectively mitigate these dangers and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Key points include:
- The necessity of using FDA-approved sharps containers
- Establishing regular collection schedules
- Ensuring that staff are well-trained on safety protocols
Statistics reveal the alarming frequency of needlestick incidents, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive safety measures to prevent exposure to bloodborne pathogens. Furthermore, compliance with OSHA and EPA regulations is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment and avoiding legal repercussions.
Given these insights, healthcare facilities must prioritize robust disposal methods and continuous staff education. A proactive approach not only safeguards personnel health but also enhances overall patient safety and environmental sustainability. By fostering a culture of safety and compliance, healthcare organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with medical sharps, ultimately improving the quality of care provided.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are medical sharps and why are they risky?
Medical sharps include instruments like needles, syringes, and scalpel blades that pose significant risks in medical settings due to the potential for needlestick accidents, which can lead to the transmission of serious bloodborne pathogens such as HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
How prevalent are needlestick incidents among healthcare professionals?
Needlestick incidents account for over 80% of all percutaneous exposure occurrences in the United States, with approximately 385,000 reported annually among healthcare workers, indicating a major occupational hazard.
What are the risks associated with needlestick incidents?
The risk of contracting hepatitis C following a sharps incident is about 1.8%, while the risk of HIV transmission is approximately 0.3%. Injection pens are responsible for 39% of needlestick incidents related to subcutaneous injections.
What are some statistics that highlight the need for safety protocols in medical environments?
Hospitals report about 5-10 needlestick incidents annually per 100 beds, and research indicates that 33% of all needle-related incidents occur during waste removal, emphasizing the need for proper handling practices.
What measures can medical facilities take to mitigate risks associated with medical sharps?
Medical facilities should implement robust waste management protocols, including the use of FDA-approved containers that are closable, puncture-resistant, and leak-proof. Staff education on safe handling practices and prompt disposal is also essential.
What role does ongoing training play in preventing needlestick incidents?
Ongoing training initiatives regarding bloodborne pathogen exposure, as mandated by OSHA, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) are critical components of a comprehensive safety strategy to protect healthcare workers and patients.
What common errors in needlestick prevention should be addressed?
Frequent errors include recapping needles and improper handling, which must be addressed to enhance the safety culture within medical environments.
