Introduction
Effective biomedical waste management is essential not only for regulatory compliance but also for protecting public health and the environment. In regions such as Latin America and the Caribbean, a staggering 70% of medical waste is poorly managed, leading to significant risks, including the transmission of infectious diseases and environmental contamination. This article explores best practices for managing biomedical waste, providing insights into effective strategies that healthcare facilities can implement to mitigate these risks. Organizations must consider how to ensure compliance with evolving regulations while safeguarding both their staff and the communities they serve.
Understand the Importance of Biomedical Waste Management
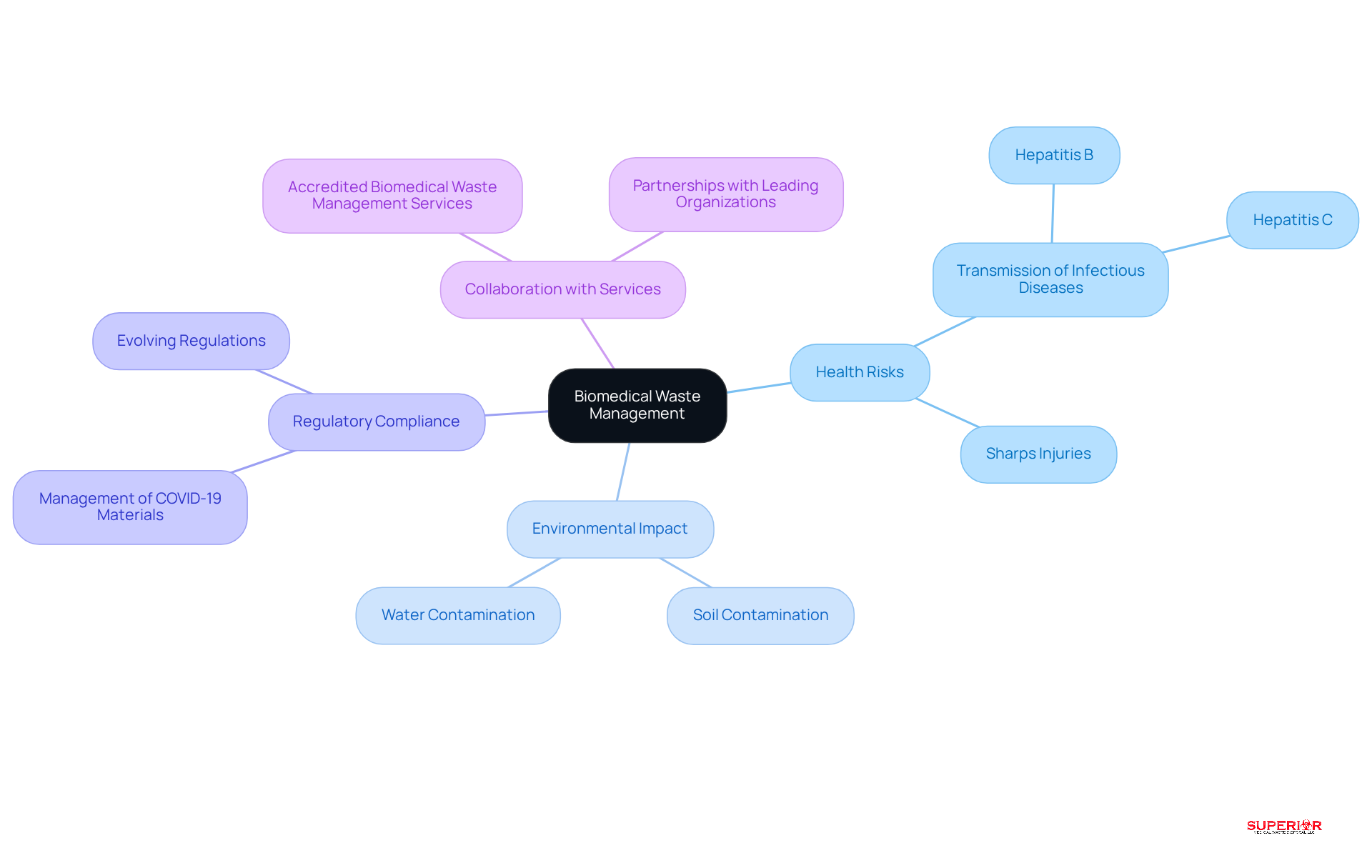
Effective biomedical refuse management is essential for safeguarding public health and protecting the environment. Improper disposal of biomedical materials presents significant health risks, including the transmission of infectious diseases such as Hepatitis B and C, particularly through sharps that can cause injuries.
Alarmingly, 70% of medical refuse generated in Latin America and the Caribbean is inadequately managed, which can lead to potential public health crises. Additionally, hazardous substances from biomedical refuse can leach into soil and water systems, resulting in long-term environmental contamination that impacts both ecosystems and human health.
For example, untreated medical refuse can enter municipal disposal systems, jeopardizing groundwater quality and increasing the risk of disease transmission. As healthcare facilities face increasing scrutiny from regulatory bodies, it is crucial that they recognize their responsibility in utilizing biomedical waste management services effectively. This not only mitigates health concerns but also ensures compliance with evolving regulations, particularly regarding the management of COVID-19 materials, which include vaccines, testing supplies, and potentially contaminated personal protective equipment.
Collaborating with accredited biomedical waste management services, such as Superior Medical Waste Disposal, is vital to ensure compliance and minimize health risks. Our extensive network of partnerships with leading organizations in the medical field enhances our expertise and commitment to regulatory compliance and environmental sustainability. Ultimately, this collaboration fosters a safer environment for both healthcare providers and the communities they serve.
Identify Types of Biomedical Waste and Their Risks
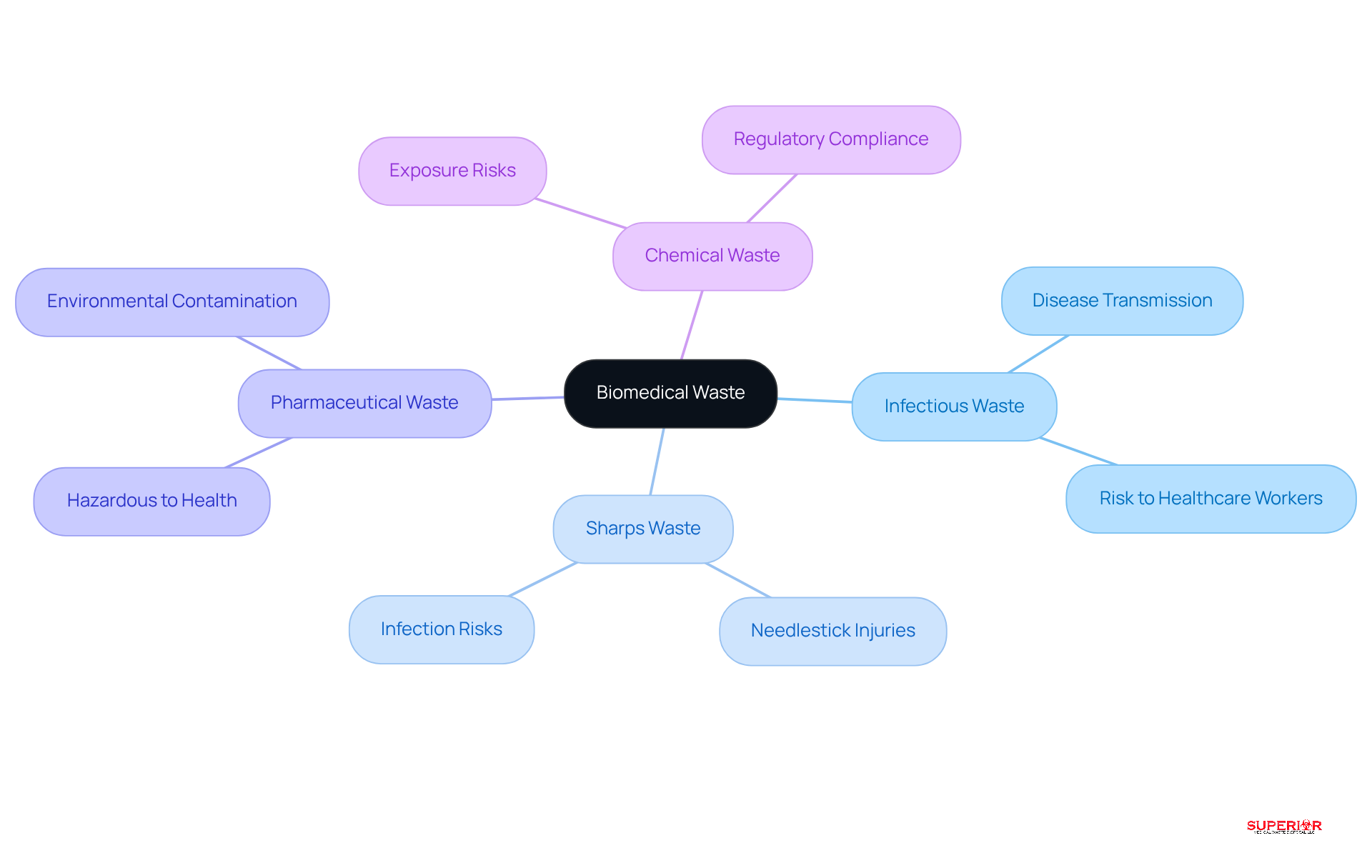
Biomedical waste encompasses various categories, each presenting unique challenges that require careful management. The key types include:
-
Infectious Waste: This category comprises materials contaminated with pathogens, such as blood-soaked bandages and cultures, which pose a significant risk of disease transmission. Proper handling and disposal are critical to preventing outbreaks and protecting both healthcare workers and patients.
-
Sharps Waste: Items like needles, scalpels, and other sharp instruments can cause injuries and infections if not managed correctly. The risk of needlestick injuries underscores the importance of strict disposal protocols and the use of puncture-resistant containers.
-
Pharmaceutical Waste: Expired or unused medications can be hazardous to health and the environment if disposed of improperly. Healthcare facilities must adhere to specific guidelines for pharmaceutical disposal management to mitigate risks associated with drug diversion and environmental contamination.
-
Chemical Waste: Hazardous chemicals used in healthcare settings require specialized handling and disposal methods to prevent exposure and environmental harm. Compliance with regulations regarding chemical disposal is essential for maintaining safety standards.
Each category of biomedical waste requires specific biomedical waste management services to effectively minimize risks. This underscores the importance of thorough training and ongoing awareness among medical personnel, ensuring they are equipped to manage waste responsibly and in accordance with evolving regulations. As the medical landscape continues to change, staying informed about best practices in waste management is vital for safeguarding public health and the environment.
Implement Best Practices for Waste Segregation and Disposal
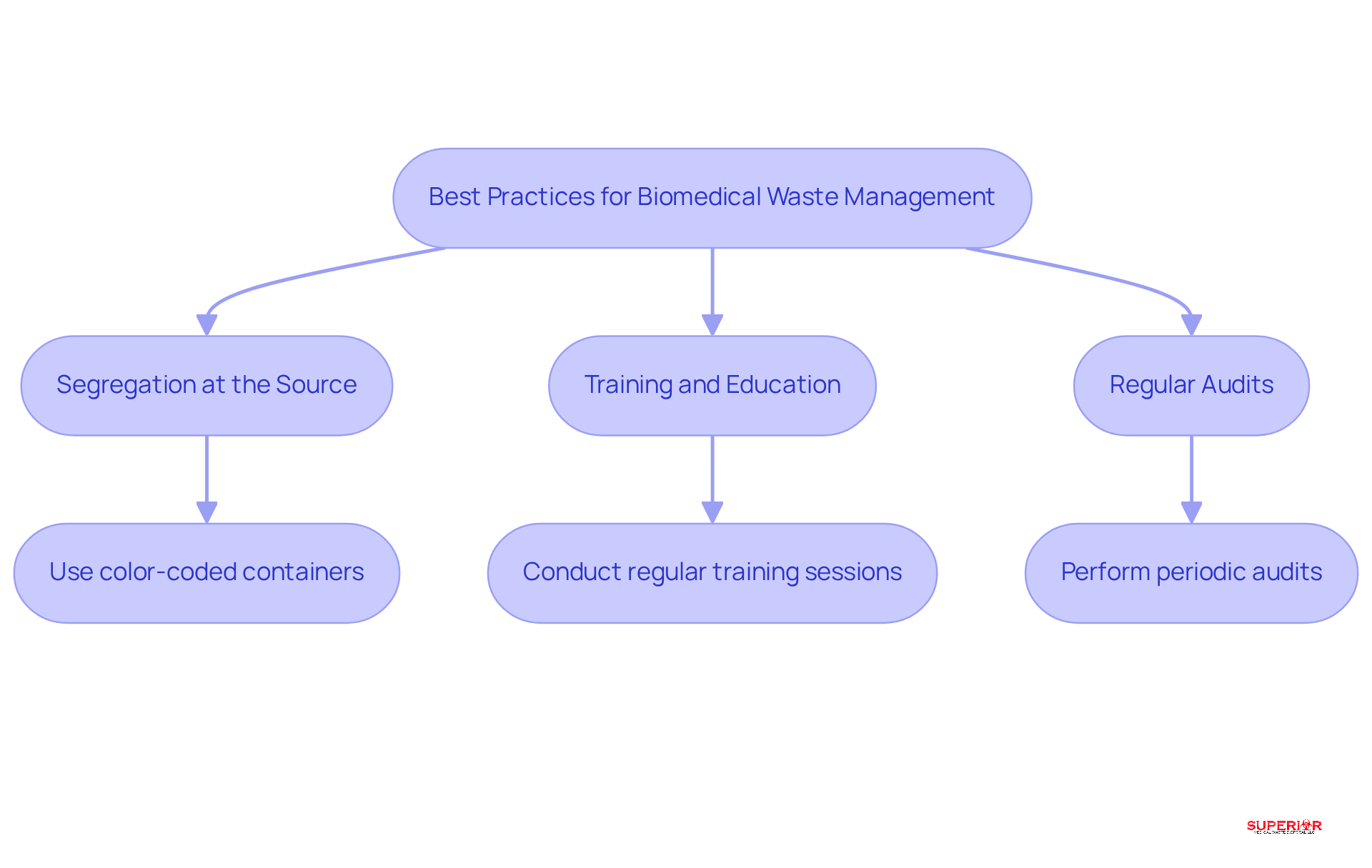
To effectively manage biomedical waste, healthcare facilities should adopt several best practices:
-
Segregation at the Source: Waste must be separated at the point of generation to prevent contamination. Utilizing color-coded containers – red for infectious materials and yellow for sharps – ensures clear identification and minimizes the risk of improper disposal. This practice not only enhances safety but also streamlines resource management workflows, reducing confusion among staff.
-
Training and Education: Regular training sessions for staff on proper waste segregation and disposal techniques are essential. Comprehensive training programs ensure that all employees understand the importance of compliance and safety, fostering a culture of responsibility. Facilities that prioritize training often experience improved compliance confidence and reduced material volumes over time with the implementation of biomedical waste management services. According to OSHA, millions of healthcare workers face the ongoing threat of occupational exposure to bloodborne pathogens due to sharps injuries, highlighting the critical need for effective training.
-
Regular Audits: Conducting periodic reviews of disposal management practices is crucial for identifying areas for improvement and ensuring adherence to established protocols. These audits allow facilities to transition from reactive to preventive compliance, addressing vulnerabilities before they escalate into regulatory risks. Engaging in audits at the beginning of the year can establish a standard for operational efficiency and compliance, as January provides healthcare facilities with a unique opportunity to stabilize workflows and proactively assess medical disposal practices.
The organization provides essential biomedical waste management services to ensure safe disposal. Partnership with certified disposal services, including biomedical waste management services like Superior Medical Disposal, ensures that materials are treated and discarded in accordance with regulatory standards. This partnership not only enhances safety but also ensures that facilities remain compliant with state and federal guidelines, thereby reducing hazards associated with improper disposal. Furthermore, engaging with our extensive network of collaborations with prominent entities in the medical field further strengthens compliance and operational effectiveness.
By implementing these practices, medical facilities can significantly mitigate the risks associated with biomedical waste and enhance their overall compliance, ultimately creating a safer environment for both personnel and patients.
Navigate Regulatory Compliance in Biomedical Waste Management
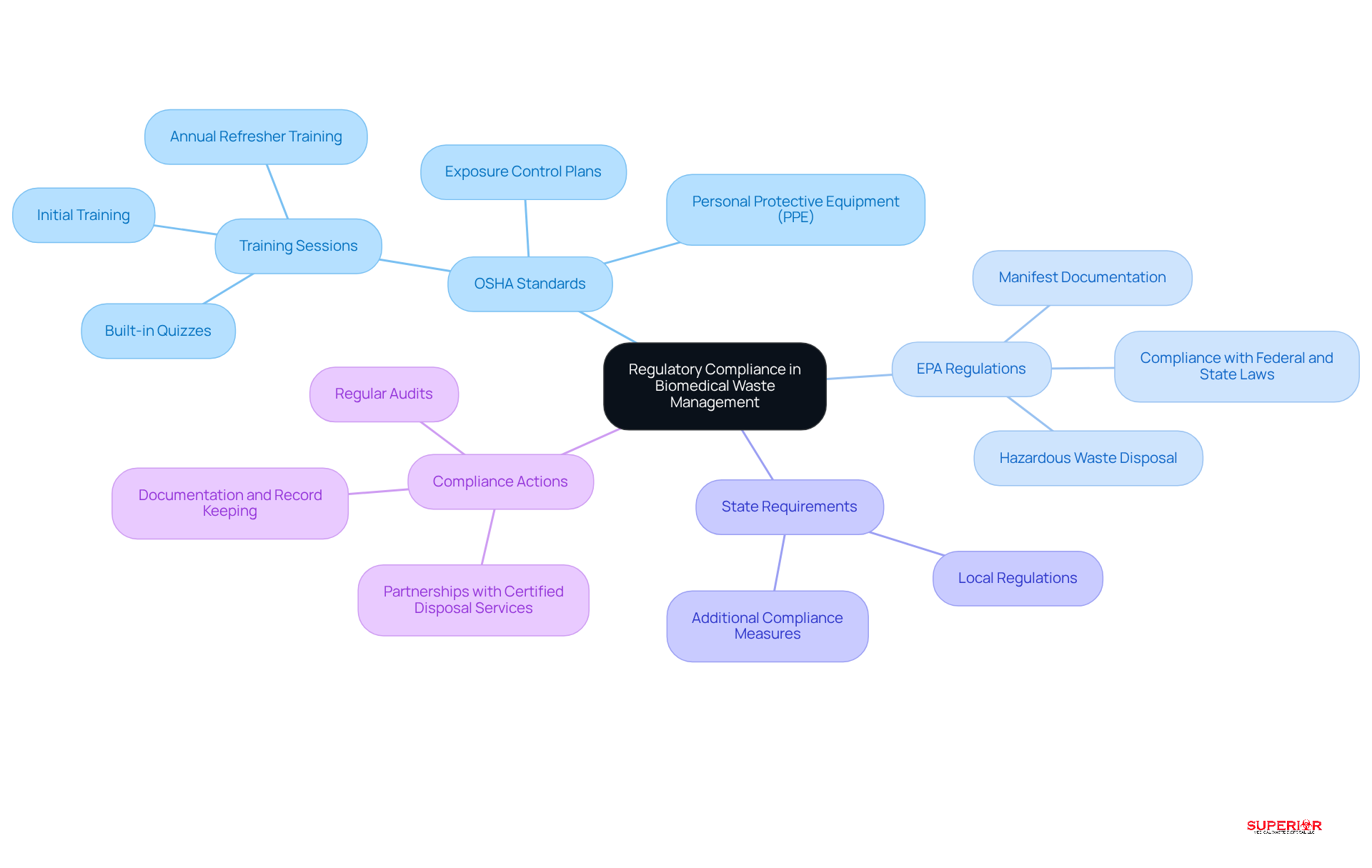
Healthcare facilities operate within a complex regulatory framework that governs biomedical waste management services. This framework is essential for ensuring safety and compliance in healthcare settings.
OSHA Standards: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates that healthcare facilities implement stringent safety measures to protect workers from exposure to hazardous waste. This includes comprehensive training for staff on proper handling procedures and the mandatory use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees biomedical waste management services for the disposal of hazardous materials, including biomedical refuse, to ensure compliance with federal and state laws. Adhering to these regulations is crucial for facilities to avoid civil penalties and to maintain safe disposal practices.
In addition to federal regulations, each state may impose additional requirements regarding biomedical waste management services. Healthcare facilities must familiarize themselves with local laws to ensure thorough adherence.
To navigate these regulations effectively, healthcare providers should establish a robust compliance program. This program should include:
- Regular training sessions
- Audits
- Partnerships with certified disposal services
Such a proactive approach not only ensures adherence to regulatory standards but also enhances the safety and sustainability of waste management practices, ultimately protecting both staff and patients.
Conclusion
Effective biomedical waste management is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is essential for safeguarding public health and protecting the environment. Understanding the various types of biomedical waste and their associated risks enables healthcare facilities to implement measures that mitigate potential hazards. Adopting best practices such as waste segregation, staff training, and regular audits is crucial for ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and enhancing the safety of healthcare environments.
This article has underscored the significance of proper biomedical waste management. Key points include the identification of different waste categories – infectious, sharps, pharmaceutical, and chemical – and the unique challenges each presents. The necessity of adhering to regulatory frameworks established by OSHA and the EPA has also been highlighted, emphasizing the importance for healthcare facilities to develop robust compliance programs and collaborate with certified disposal services.
Ultimately, effective biomedical waste management is a collective responsibility that affects not only healthcare providers but also the communities they serve. By prioritizing safety, compliance, and environmental sustainability, healthcare facilities can contribute to a healthier future. It is imperative for all stakeholders to remain vigilant and committed to best practices in biomedical waste management, thereby ensuring the well-being of both patients and the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is biomedical waste management important?
Biomedical waste management is crucial for safeguarding public health and protecting the environment. Improper disposal can lead to significant health risks, including the transmission of infectious diseases and environmental contamination.
What are the health risks associated with improper biomedical waste disposal?
Improper disposal of biomedical materials can transmit infectious diseases such as Hepatitis B and C, especially through sharps that can cause injuries.
What percentage of medical waste in Latin America and the Caribbean is inadequately managed?
Alarmingly, 70% of medical refuse generated in Latin America and the Caribbean is inadequately managed.
What environmental impacts can result from untreated biomedical waste?
Hazardous substances from untreated biomedical waste can leach into soil and water systems, leading to long-term environmental contamination that affects ecosystems and human health.
How can untreated medical refuse affect municipal disposal systems?
Untreated medical refuse can enter municipal disposal systems, jeopardizing groundwater quality and increasing the risk of disease transmission.
What is the role of healthcare facilities in biomedical waste management?
Healthcare facilities have a responsibility to utilize biomedical waste management services effectively to mitigate health concerns and ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
What specific materials require careful management due to COVID-19?
Materials such as vaccines, testing supplies, and potentially contaminated personal protective equipment require careful management due to COVID-19.
How can organizations ensure compliance with biomedical waste management regulations?
Collaborating with accredited biomedical waste management services, like Superior Medical Waste Disposal, is vital for ensuring compliance and minimizing health risks.
What benefits come from partnerships with biomedical waste management services?
Collaborating with these services enhances expertise in regulatory compliance and environmental sustainability, fostering a safer environment for healthcare providers and the communities they serve.
