Introduction
Understanding the complexities of medical waste disposal is essential for healthcare facilities committed to safeguarding public health and the environment. As healthcare activities increase, so does the volume of medical waste generated, underscoring the urgent need for effective disposal methods that prioritize safety and compliance. Healthcare providers face the challenge of navigating a complex landscape of regulations and best practices while minimizing the risks associated with improper waste management.
This article outlines five essential steps for the safe disposal of medical waste. By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can implement robust waste management strategies that protect both their facilities and the communities they serve.
Define Medical Waste and Its Types
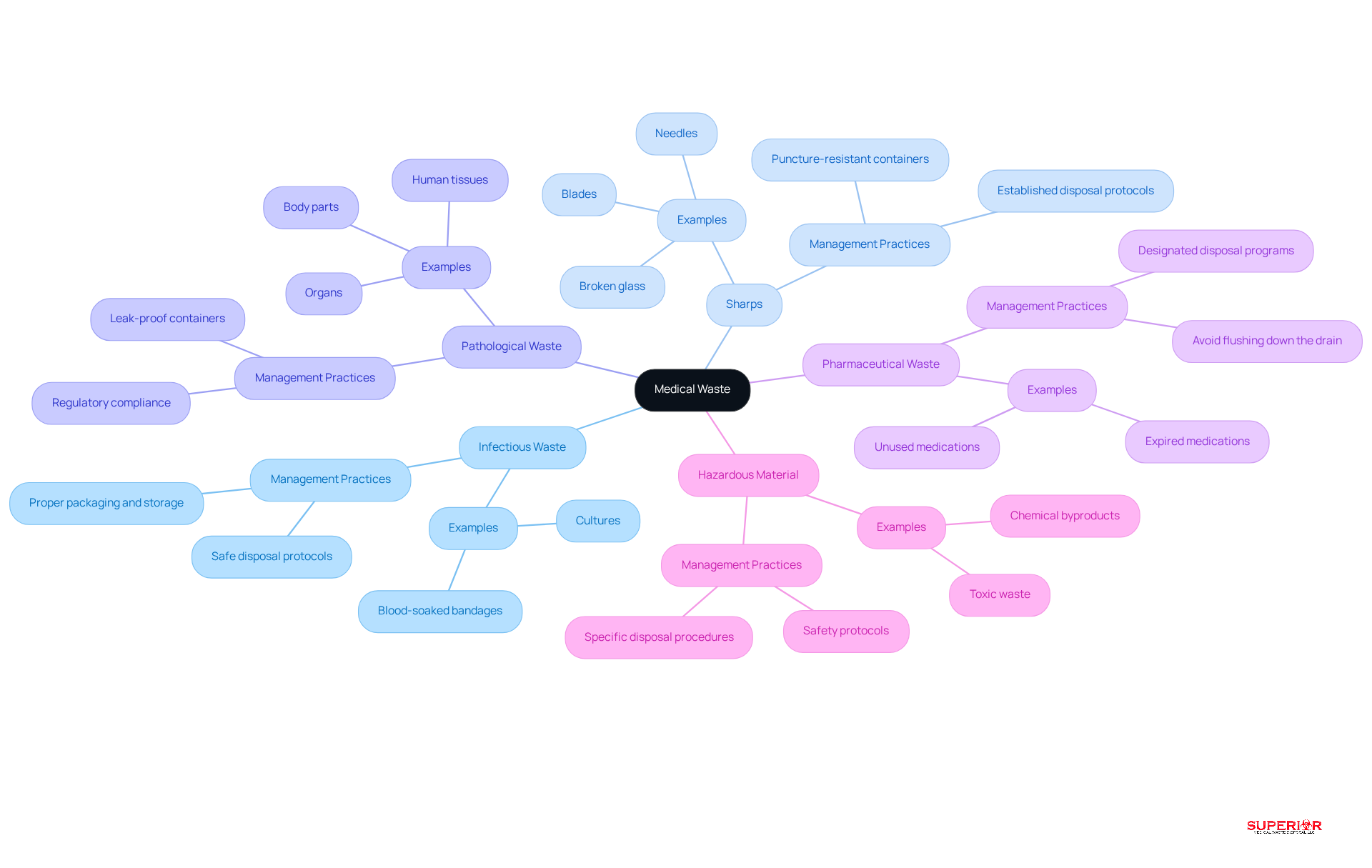
Medical refuse encompasses any material generated during the diagnosis, treatment, or immunization of humans or animals. Accurately categorizing this refuse is essential for ensuring the safe and compliant disposal of medical waste. The primary categories include:
-
Infectious Waste: This category includes materials capable of transmitting infectious diseases, such as blood-soaked bandages and cultures. Approximately 15% of healthcare waste is classified as hazardous, with a significant portion being infectious. Proper packaging and storage techniques are crucial to ensure safe disposal of medical waste and prevent exposure.
-
Sharps: Items that can puncture or cut skin, including needles, blades, and broken glass, fall under this category. Effective management of sharps is vital to ensure the safe disposal of medical waste, preventing injuries and the transmission of blood-borne pathogens. Sharps should be placed in puncture-resistant containers and disposed of according to established protocols to mitigate risks.
-
Pathological Waste: This category consists of human tissues, organs, and body parts removed during surgical procedures or autopsies. Managing pathological materials is critical to prevent environmental contamination and health risks. These materials should be stored in leak-proof containers and treated according to regulatory guidelines for the disposal of medical waste.
-
Pharmaceutical Waste: Expired or unused medications require special handling to mitigate risks to human health and the environment. Improper disposal of pharmaceutical materials can lead to water contamination and the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. These materials should be separated and discarded through designated pharmaceutical disposal programs.
-
Hazardous Material: This includes refuse that poses a risk to human health or the environment, such as chemical byproducts from laboratories. Efficient handling of hazardous materials is essential to avoid negative health impacts and ecological harm. It is important to follow specific procedures for the disposal of medical waste to ensure safety.
Understanding these classifications is crucial for healthcare professionals to implement effective practices for the disposal of medical waste, ensuring adherence to regulations and protecting public health. All staff managing bloodborne pathogens must undergo training, which should be documented according to the facility’s disposal management plan and made accessible for review for at least three years.
Implement Proper Waste Segregation Practices
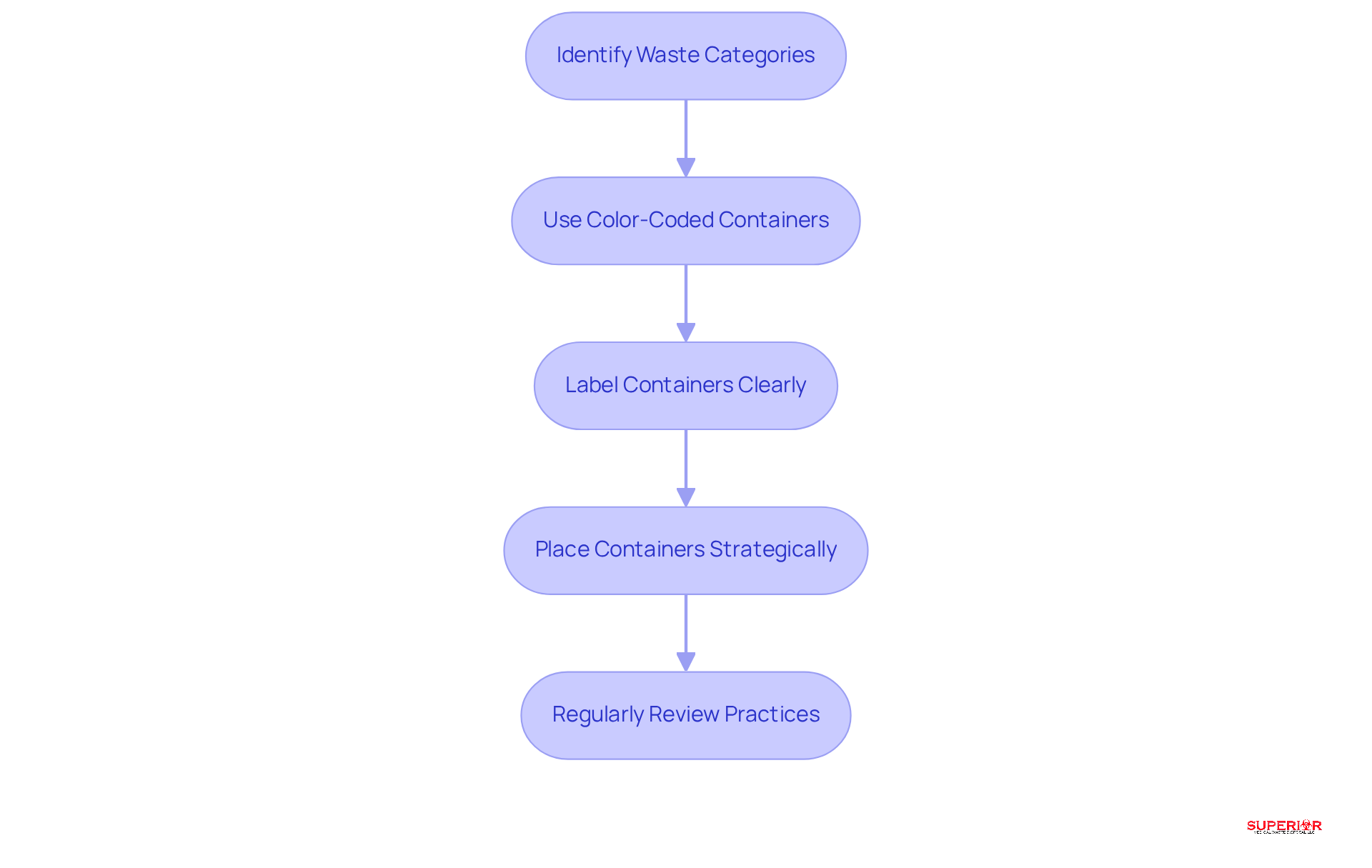
To implement effective waste segregation practices, follow these steps:
-
Identify waste categories: Train staff to recognize various types of medical refuse, including sharps, biohazardous materials, and pharmaceuticals, along with the appropriate disposal of medical waste methods for each. It is essential to understand that unused or expired pharmaceuticals are classified as pharmaceutical disposal, not biohazard disposal, and must be handled separately according to state regulations.
-
Use Color-Coded Containers: Designate specific containers for each type of refuse, employing a color-coded system – red for infectious materials, yellow for sharps, and blue for non-hazardous pharmaceuticals – to minimize the risk of cross-contamination. This approach significantly enhances adherence and safety in refuse handling.
-
Label Containers Clearly: Ensure all refuse containers are distinctly marked with hazard warnings and types to eliminate confusion and promote proper handling practices among staff, reinforcing compliance with regulations.
-
Place Containers Strategically: Position refuse containers near the source of material generation, encouraging staff to dispose of items properly and swiftly. This practice decreases the chances of improper disposal of medical waste and ensures compliance with disposal protocols.
-
Regularly Review Practices: Conduct periodic audits of refuse segregation practices to identify areas for improvement. This ongoing evaluation is essential for ensuring adherence to changing regulations and enhancing overall resource management efficiency. Recent studies indicate that consistent training and evaluations can lead to improved segregation practices and reduced risks associated with healthcare refuse.
Choose Appropriate Disposal Methods
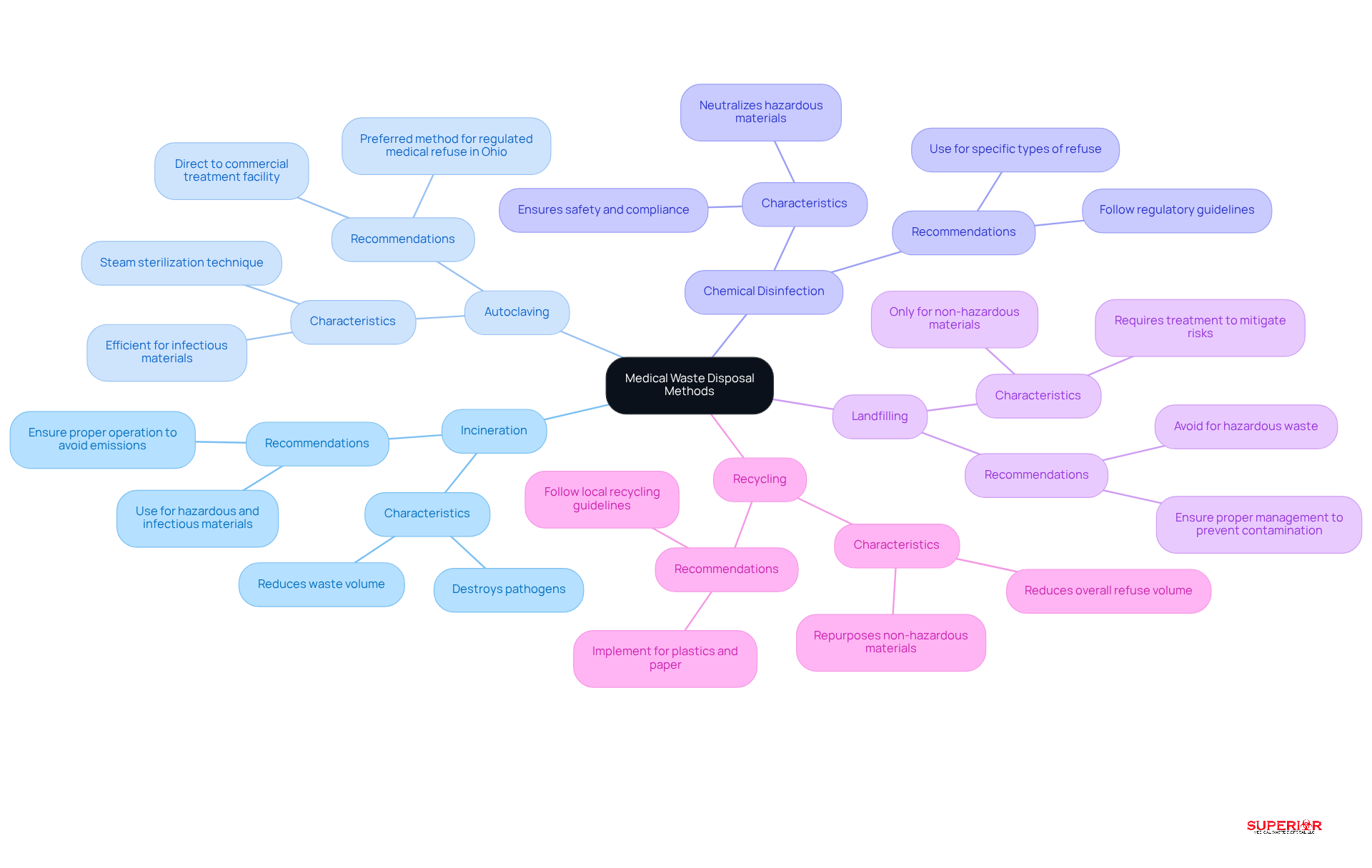
Selecting the appropriate disposal of medical waste method requires a thorough understanding of the waste’s characteristics and the available treatment options.
-
Incineration is a prevalent method for treating hazardous and infectious materials. This process effectively reduces waste volume while destroying pathogens, making it a reliable choice for many healthcare facilities.
-
Autoclaving, a steam sterilization technique, is particularly efficient for managing infectious materials. It renders these materials non-hazardous prior to disposal. In Ohio, the Ohio EPA recommends that all infectious materials be directed to a commercial treatment facility, with the disposal of medical waste through autoclaving identified as the preferred method for regulated medical refuse (RMR).
-
Chemical Disinfection is suitable for specific types of refuse, as it can neutralize hazardous materials before disposal. This method is essential for ensuring safety and compliance with regulations.
-
Landfilling should only be considered for non-hazardous materials. It is crucial that these materials are treated to mitigate any potential environmental risks.
-
Lastly, Recycling presents opportunities for reducing overall refuse volume by repurposing non-hazardous materials such as plastics and paper.
Each method for the disposal of medical waste has its advantages and limitations. Therefore, it is vital to select the appropriate method based on the specific type of refuse and the regulatory requirements, particularly those established by the Ohio EPA.
Ensure Compliance with Regulatory Standards
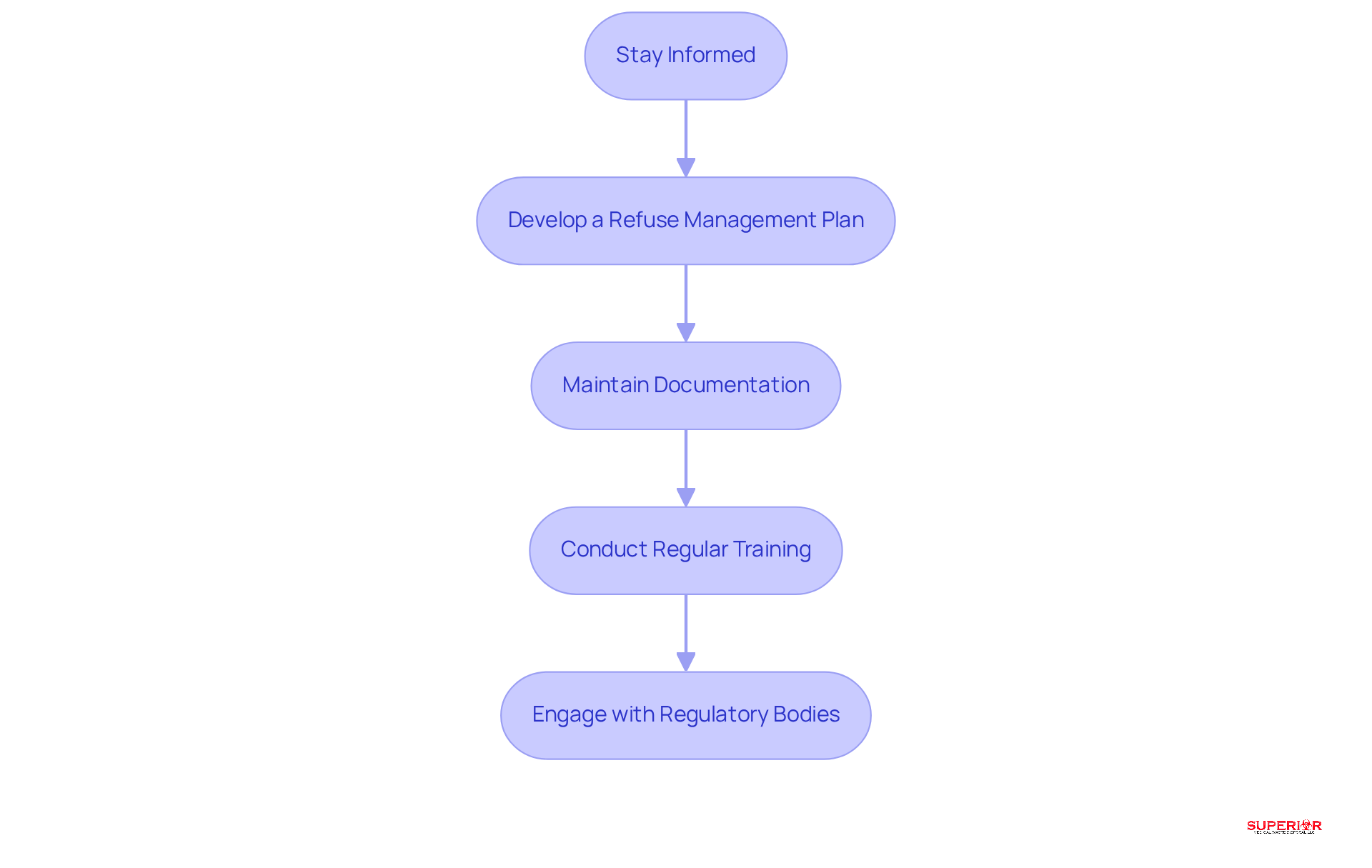
To ensure compliance with regulatory standards, healthcare facilities should take the following steps:
-
Stay informed by regularly reviewing local, state, and federal regulations regarding the disposal of medical waste management, particularly Ohio EPA regulations, to remain compliant with any changes.
-
Develop a Refuse Management Plan that outlines procedures for the disposal of medical waste, including segregation, storage, transportation, and elimination. Effective plans are tailored to the specific needs of the facility and can significantly enhance operational efficiency, especially when utilizing services from Superior Medical Waste Disposal.
-
Maintain Documentation: Accurate records of refuse generation, treatment, and disposal are crucial. These documents not only demonstrate adherence during inspections but also assist in recognizing trends and areas for enhancement in the disposal of medical waste.
-
Conduct Regular Training: Ongoing training for staff on compliance requirements and best practices is vital. Statistics indicate that most healthcare disposal violations arise from insufficient training, making regular sessions essential for ensuring safety and compliance.
-
Engage with Regulatory Bodies: Establishing communication with local health departments and regulatory agencies ensures adherence to guidelines and provides updates on regulatory changes. This proactive approach can assist facilities in navigating the complex environment of healthcare refuse handling effectively.
Provide Staff Training and Education
To effectively train staff on medical waste management in Traverse City healthcare facilities, it is essential to follow a structured approach:
-
Develop a Training Program: Establish a comprehensive training initiative that covers all aspects of healthcare refuse handling. This includes identification, segregation, and techniques for the disposal of medical waste tailored to the specific types of refuse generated by local establishments, such as Munson and Byers Heather, with a focus on biohazard materials and sharps.
-
Employ Diverse Training Techniques: Utilize a variety of training methods, including online courses, practical workshops, and informational sessions. This approach accommodates different learning styles and ensures that staff are well-informed about the unique challenges associated with handling health-related refuse in Traverse City.
-
Assess Knowledge Retention: Implement evaluations or quizzes to measure staff understanding of medical disposal practices and compliance requirements. This step is crucial to ensure they are equipped for the disposal of medical waste, including biohazard materials and sharps.
-
Offer Refresher Courses: Schedule regular refresher courses to keep staff updated on the latest regulations and best practices, particularly those relevant to the specific refuse streams produced by Traverse City healthcare providers.
-
Encourage a Culture of Safety: Create an environment where staff feel comfortable discussing waste management issues and reporting concerns. This culture promotes continuous improvement in waste handling practices, which is vital for maintaining compliance and safety in local healthcare settings.
Conclusion
Implementing safe disposal practices for medical waste is not merely a regulatory requirement; it is essential for public health and environmental protection. By understanding the various types of medical waste and adhering to structured disposal methods, healthcare facilities can significantly reduce the risks associated with hazardous materials. Proper waste segregation, appropriate disposal techniques, and compliance with regulatory standards are crucial steps in safeguarding both staff and the community.
This guide has outlined five critical steps for the safe disposal of medical waste:
- Defining waste types
- Implementing effective segregation practices
- Selecting suitable disposal methods
- Ensuring compliance with regulations
- Providing comprehensive staff training
Each of these elements is vital in creating a safe and efficient waste management system. By employing color-coded systems, maintaining clear documentation, and regularly training staff, healthcare facilities can enhance their waste management practices and minimize the likelihood of violations.
The significance of these practices extends beyond mere compliance; they are fundamental to protecting human health and the environment. As healthcare providers navigate the complexities of medical waste disposal, it is imperative to prioritize the development of robust waste management strategies. Engaging in ongoing education and fostering a culture of safety will not only ensure adherence to current regulations but also promote a sustainable approach to waste disposal that benefits the entire community.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is medical waste?
Medical waste encompasses any material generated during the diagnosis, treatment, or immunization of humans or animals.
What are the primary types of medical waste?
The primary types of medical waste include infectious waste, sharps, pathological waste, pharmaceutical waste, and hazardous material.
What is infectious waste?
Infectious waste includes materials capable of transmitting infectious diseases, such as blood-soaked bandages and cultures, and constitutes approximately 15% of healthcare waste.
How should sharps be managed?
Sharps, which include items like needles and broken glass, should be placed in puncture-resistant containers and disposed of according to established protocols to prevent injuries and the transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
What constitutes pathological waste?
Pathological waste consists of human tissues, organs, and body parts removed during surgical procedures or autopsies, and it must be managed to prevent environmental contamination and health risks.
How should pharmaceutical waste be handled?
Expired or unused medications should be separated and discarded through designated pharmaceutical disposal programs to mitigate risks to human health and the environment.
What is considered hazardous material in medical waste?
Hazardous material includes refuse that poses a risk to human health or the environment, such as chemical byproducts from laboratories, requiring specific disposal procedures.
Why is proper waste segregation important?
Proper waste segregation is crucial for ensuring safe and compliant disposal of medical waste, protecting public health, and adhering to regulations.
What steps can be taken to implement effective waste segregation practices?
Effective waste segregation practices include training staff to recognize waste categories, using color-coded containers, labeling containers clearly, strategically placing containers, and regularly reviewing practices.
What color codes are used for waste containers?
Red is used for infectious materials, yellow for sharps, and blue for non-hazardous pharmaceuticals.
How often should waste segregation practices be reviewed?
Waste segregation practices should be reviewed periodically to identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with changing regulations.
